BROWSE TOPICS
Introduction
In today’s digital age, data is a critical asset for organizations across industries. Data management involves a set of practices, processes, and technologies used to collect, organize, store, and maintain data to ensure its accessibility, accuracy, and security. Effective data management enables businesses to make informed decisions, comply with regulations, improve operational efficiency, and protect sensitive information. This guide covers everything from the basics of data management to strategies, tools, and future trends that organizations must know to manage their data effectively.What is Data Management?
Key Objectives of Data Management:
- Data Accuracy: Ensuring that data is correct and up-to-date.
- Data Accessibility: Making data easily available to authorized users.
- Data Security: Protecting data from unauthorized access or breaches.
- Compliance: Ensuring that data practices comply with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA.
Importance of Data Management

Data management is essential for organizations to achieve operational efficiency, data security, and regulatory compliance. Here’s why it matters:
1. Informed Decision-Making
Data-driven decision-making is a cornerstone of modern business. Organizations can use well-managed data to analyze trends, predict outcomes, and make better decisions.
2. Operational Efficiency
Proper data management reduces the time and effort spent searching for information. Organized and accessible data improves productivity across departments.
3. Compliance and Risk Management
Data management ensures that organizations comply with data privacy regulations, reducing the risk of fines and legal issues.
4. Data Security
Implementing data security measures through data management protects sensitive information from breaches and cyberattacks.
5. Data Quality
Maintaining data accuracy and completeness is essential for building trust in the insights derived from data.
Key Components of Data Management
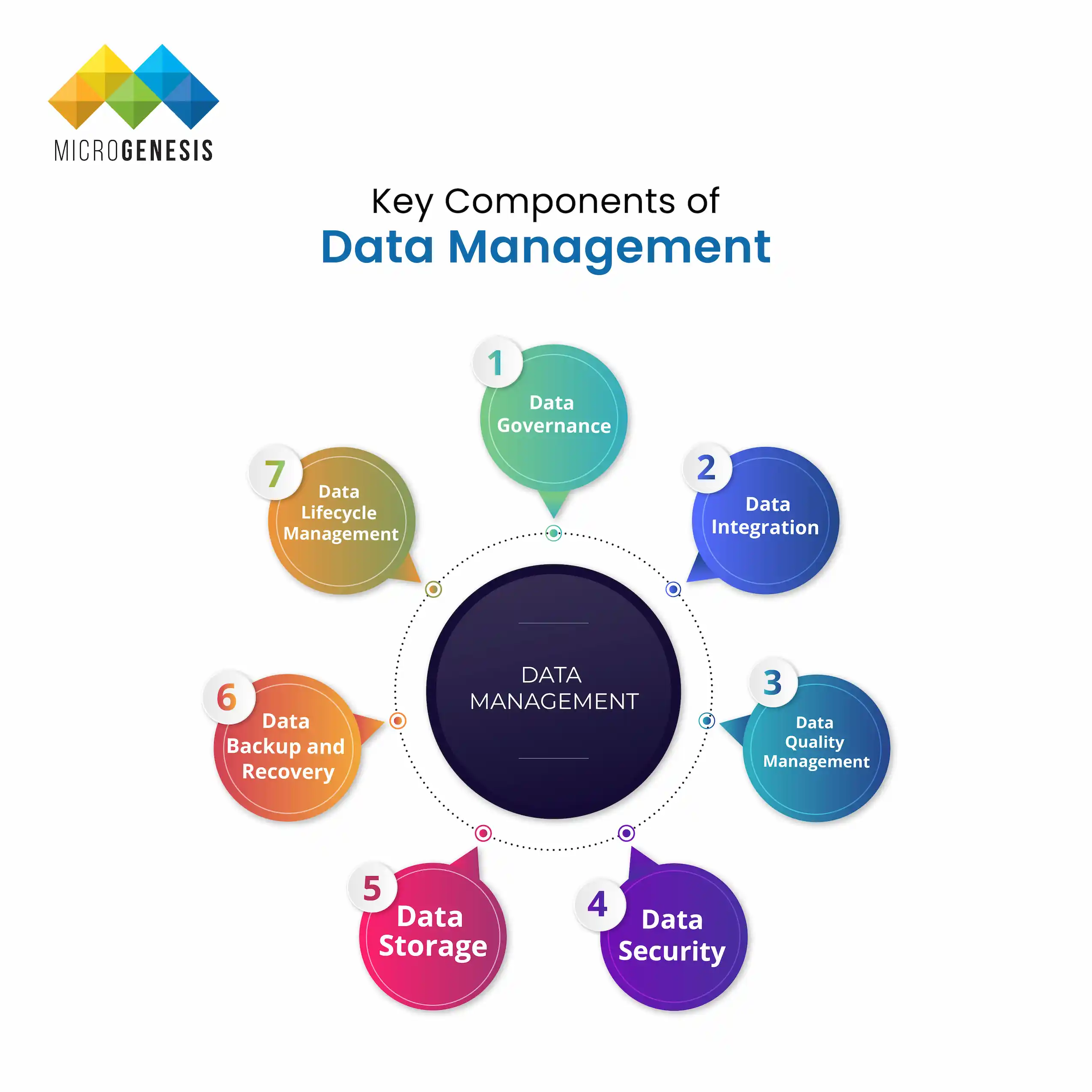
Data management consists of several core components that ensure the proper handling of data throughout its lifecycle.
1. Data Governance
Data governance refers to policies, procedures, and roles that ensure data is managed responsibly. It sets rules for data usage, security, and privacy.
2. Data Integration
Data integration involves combining data from multiple sources into a unified view. This process ensures that businesses can access comprehensive and accurate data.
3. Data Quality Management
Data quality management focuses on ensuring that data is accurate, complete, and consistent. Processes like data validation and cleansing are critical here.
4. Data Security
Data security includes implementing access controls, encryption, and monitoring to protect data from breaches and unauthorized access.
5. Data Storage
Data storage refers to how and where data is kept, whether in databases, data warehouses, or cloud solutions.
6. Data Backup and Recovery
Data backup and recovery ensures that data can be restored in case of loss or corruption, which is crucial for disaster recovery plans.
7. Data Lifecycle Management
Data lifecycle management covers data creation, usage, retention, and deletion. It ensures that data is handled responsibly at every stage.
Types of Data Management
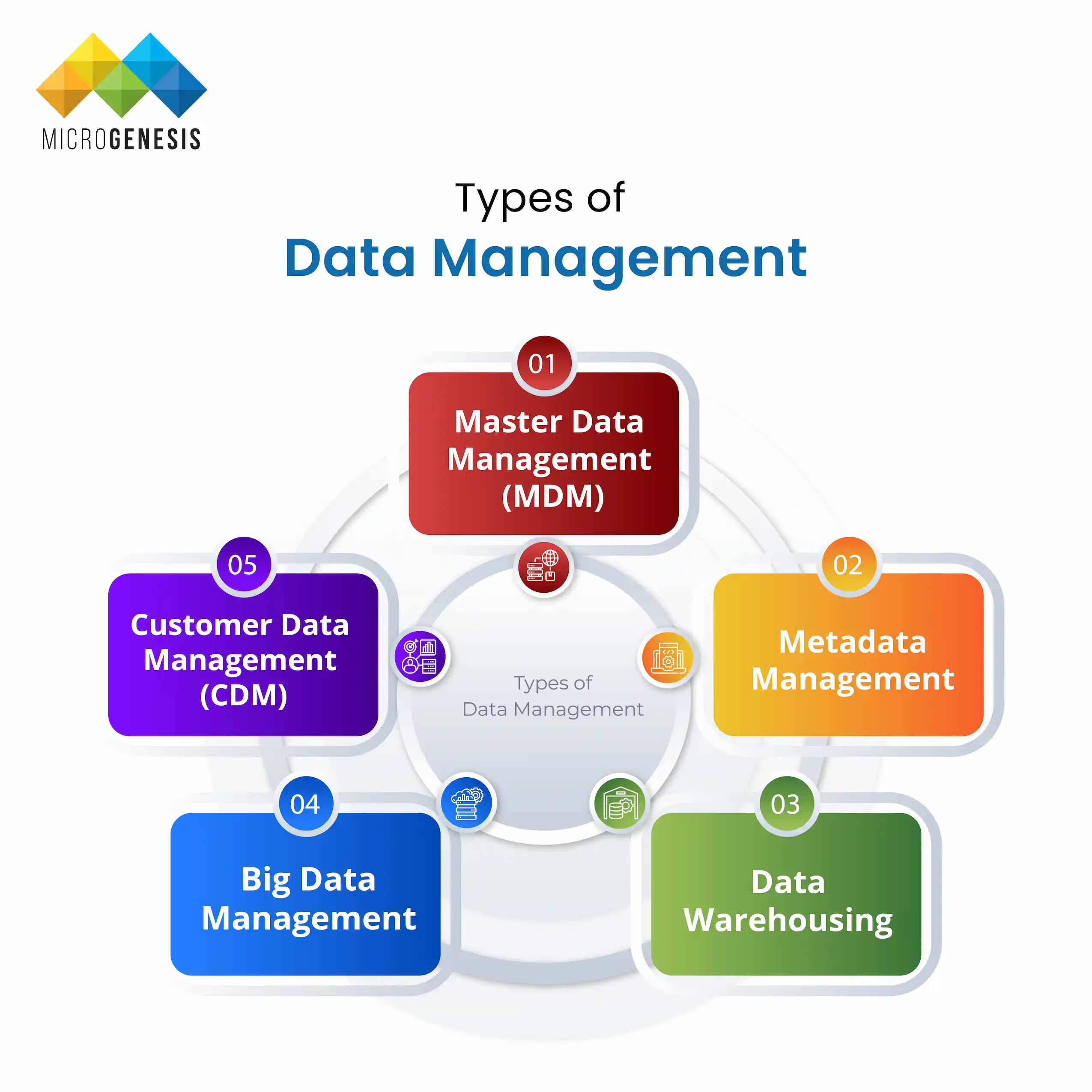
Different types of data management address various organizational needs. Here are some key types:
1. Master Data Management (MDM)
MDM focuses on creating a single source of truth for core business data, such as customer or product information.
2. Metadata Management
This involves managing data about data, like file descriptions and categorizations, to make data easier to find and use.
3. Data Warehousing
Data warehousing involves storing large volumes of structured data in a central repository for analysis and reporting.
4. Big Data Management
Big data management addresses large volumes of unstructured and structured data, often using real-time analytics.
5. Customer Data Management (CDM)
CDM focuses on managing customer information to improve customer relationships and personalize experiences.
Data Management Strategies
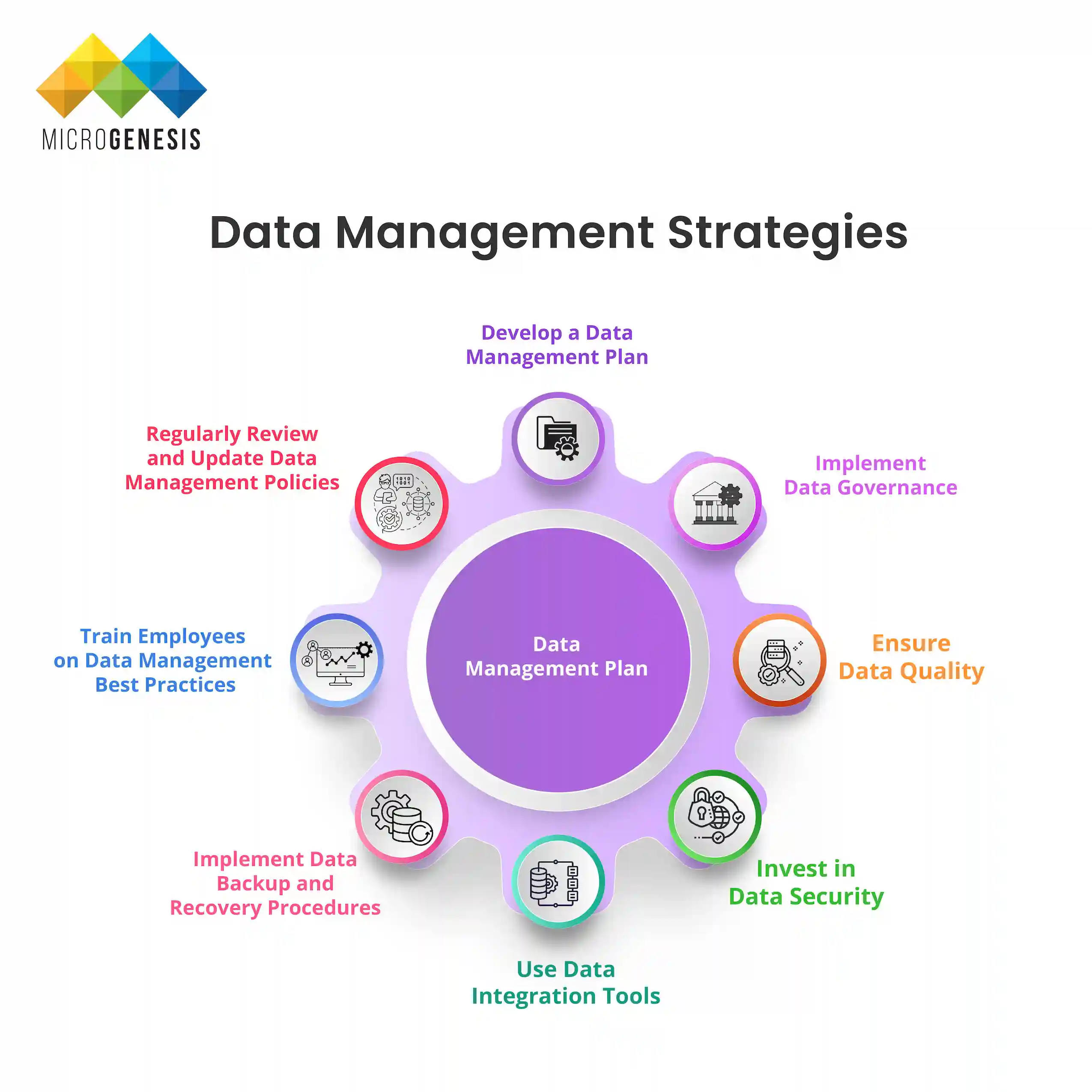
Effective data management strategies are essential for organizations to handle their data efficiently and achieve business goals. These strategies help improve data quality, security, accessibility, and compliance, ensuring that businesses can leverage their data assets for competitive advantage. Below are detailed strategies that organizations can implement to manage their data effectively.
Develop a Data Management Plan
A Data Management Plan (DMP) outlines how data will be collected, stored, managed, and used within an organization. It provides a roadmap for handling data throughout its lifecycle, ensuring consistency and accountability.
Key Elements of a Data Management Plan:
- Data Collection Methods: Define how data will be collected, including sources and formats.
- Data Storage Solutions: Identify where and how data will be stored (e.g., cloud, on-premise, hybrid).
- Data Access Controls: Determine who can access specific data sets and under what conditions.
- Data Retention Policies: Define how long data will be retained and when it will be archived or deleted.
- Data Security Measures: Outline the security protocols to protect sensitive data from breaches.
Benefits:
- Ensures data consistency and accuracy
- Reduces redundancy and data silos
- Improves data accessibility
Implement Data Governance
Data governance involves establishing policies, procedures, and standards for managing data within an organization. It ensures that data is handled responsibly and that roles and responsibilities are clearly defined.
Steps to Implement Data Governance:
- Define Data Governance Roles: Assign roles such as data stewards, data owners, and data custodians.
- Create Data Policies: Establish policies on data usage, privacy, security, and compliance.
- Ensure Regulatory Compliance: Ensure adherence to regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA.
- Monitor and Audit Data Usage: Regularly review data usage to ensure compliance and identify any issues.
Benefits:
- Enhances data quality and consistency
- Ensures compliance with legal and regulatory requirements
- Reduces risks associated with data misuse
Ensure Data Quality
Data quality management focuses on maintaining accurate, complete, and consistent data. Poor data quality can lead to incorrect insights and poor decision-making.
Steps to Ensure Data Quality:
- Data Validation: Verify that data is accurate and meets predefined criteria.
- Data Cleansing: Identify and correct errors or inconsistencies in data.
- Data Enrichment: Enhance data by adding missing information or additional context.
- Continuous Monitoring: Implement tools and processes to continuously monitor data quality.
Benefits:
- Improves decision-making accuracy
- Reduces operational inefficiencies
- Enhances customer trust and satisfaction
Invest in Data Security
Data security is critical for protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access, breaches, and cyberattacks. A strong data security strategy helps organizations safeguard their data assets.
Key Data Security Measures:
- Encryption: Secure data both in transit and at rest.
- Access Controls: Implement role-based access to limit data access to authorized personnel.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct audits to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Backup and Recovery Plans: Ensure data can be restored in case of loss or corruption.
Benefits:
- Protects sensitive data from breaches
- Ensures compliance with data privacy regulations
- Builds customer trust
Use Data Integration Tools
Data integration involves combining data from various sources to provide a unified view. It enables organizations to gain comprehensive insights and make better decisions.
Steps to Implement Data Integration:
- Identify Data Sources: Determine all internal and external data sources.
- Select Integration Tools: Use tools like Talend, Informatica, or Apache NiFi for data integration.
- Ensure Data Consistency: Implement processes to reconcile data from different sources.
- Monitor Integration Processes: Regularly check for issues in data integration workflows.
Benefits:
- Eliminates data silos
- Improves data accessibility
- Enhances data-driven decision-making
Implement Data Backup and Recovery Procedures
A robust backup and recovery strategy ensures that data can be restored in case of loss, corruption, or cyberattacks. It is essential for maintaining business continuity.
Steps to Implement Backup and Recovery:
- Identify Critical Data: Determine which data sets are essential for operations.
- Select Backup Solutions: Use tools like Veeam, Acronis, or Cohesity for data backup.
- Schedule Regular Backups: Ensure data is backed up regularly.
- Test Recovery Procedures: Conduct periodic tests to ensure data can be restored successfully.
Benefits:
- Ensures business continuity
- Reduces the impact of data loss incidents
- Protects against ransomware attacks
Train Employees on Data Management Best Practices
Employees play a critical role in data management. Providing them with the necessary training ensures that they handle data responsibly and securely.
Training Topics:
- Data Security Protocols: Teach employees how to protect sensitive data.
- Data Privacy Regulations: Ensure employees understand compliance requirements.
- Data Quality Management: Train employees on data validation and cleansing practices.
Benefits:
- Reduces the risk of data breaches due to human error
- Improves data handling practices
- Ensures compliance with regulations
Regularly Review and Update Data Management Policies
Organizations must regularly review their data management policies to adapt to changing business needs and regulatory requirements.
Steps to Review Policies:
- Conduct Policy Audits: Regularly review existing data policies.
- Update Policies: Make necessary updates based on audit findings.
- Communicate Changes: Ensure all employees are aware of policy updates.
Benefits:
- Keeps policies relevant and effective
- Ensures ongoing compliance
- Improves overall data management practices
Data Management Tools and Technologies

In the ever-evolving world of data management, various tools and technologies are essential for organizations to efficiently handle their data. These tools help ensure data is accurate, secure, and accessible.
1. Database Management Systems (DBMS)
Database Management Systems are software solutions that allow users to create, manage, and interact with databases. They provide a structured way to store and retrieve data efficiently.
Popular DBMS Tools:
- MySQL: An open-source relational database management system.
- PostgreSQL: Known for its robustness and support for complex queries.
- Oracle: A powerful commercial DBMS used by enterprises worldwide.
- MongoDB: A NoSQL database that handles unstructured data efficiently.
2. Data Integration Tools
Data integration tools combine data from various sources into a unified view, making it easier to analyze and gain insights.
Popular Data Integration Tools:
Talend: An open-source tool for data integration and data quality.
Informatica: A leading enterprise cloud data management tool.
Apache NiFi: Provides real-time data movement and transformation.
Zapier: Automates workflows by connecting different apps and data sources.
3. Data Quality Tools
Data quality tools help ensure that data is accurate, consistent, and free from errors. These tools are critical for maintaining trust in data-driven decision-making.
Popular Data Quality Tools:
Trifacta: A tool for data cleansing and preparation.
IBM InfoSphere QualityStage: Ensures high-quality data across the organization.
Ataccama ONE: Offers AI-driven data quality management.
4. Data Security Tools
Data security tools protect sensitive data from unauthorized access and breaches, ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations.
Popular Data Security Tools:
McAfee Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Prevents data breaches and protects sensitive information.
Symantec DLP: Offers comprehensive data loss prevention solutions.
IBM Guardium: Protects sensitive data across multiple environments.
5. Backup and Recovery Tools
Backup and recovery tools ensure that data is protected and can be restored in the event of data loss or corruption.
Popular Backup and Recovery Tools:
Veeam Backup & Replication: Provides fast and reliable backup and recovery.
Acronis Cyber Protect: Combines backup, cybersecurity, and endpoint protection.
Cohesity: Offers data protection and recovery solutions for hybrid environments.
Data Management Best Practices
Implementing best practices for data management helps organizations maintain data integrity, security, and accessibility.
1. Develop a Data Management Policy
Create a comprehensive policy that outlines how data will be collected, stored, accessed, and disposed of within the organization.
2. Implement Data Governance
Establish clear roles, responsibilities, and processes to ensure that data is managed responsibly and consistently.
3. Ensure Data Quality
Regularly validate, cleanse, and enrich data to maintain accuracy and consistency across all systems.
4. Invest in Data Security
Implement robust security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and regular security audits, to protect sensitive data.
5. Train Employees
Provide training on data management best practices to ensure that all employees understand their roles in managing data securely.
6. Regularly Review Policies
Periodically review and update data management policies to adapt to changing business needs and regulatory requirements.
Challenges in Data Management and How to Overcome Them
Organizations face several challenges in managing data effectively. Here are some common challenges and ways to address them:
1. Data Silos
Challenge: Data silos occur when data is isolated in different departments or systems, making it difficult to access and share information.
Solution: Implement data integration tools to break down silos and create a unified view of data.
2. Data Privacy and Compliance
Challenge: Organizations must comply with various data privacy regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA.
Solution: Implement data governance policies and use data security tools to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
3. Security Threats
Challenge: Data breaches and cyberattacks pose a significant risk to organizations.
Solution: Use data security tools, such as encryption and access controls, and conduct regular security audits.
4. Inconsistent Data Quality
Challenge: Inconsistent or inaccurate data can lead to poor decision-making.
Solution: Implement data quality management processes to validate, cleanse, and enrich data.
5. Lack of Data Literacy
Challenge: Employees may lack the skills needed to manage and analyze data effectively.
Solution: Provide regular training and education on data management best practices.
Future Trends in Data Management
The field of data management is constantly evolving. Here are some key trends that will shape the future of data management:
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML will play a significant role in automating data management tasks, improving data quality, and providing predictive insights.
2. Real-Time Data Processing
Organizations will increasingly adopt real-time data processing to make faster, data-driven decisions and improve customer experiences.
3. Blockchain for Data Security
Blockchain technology will be used to enhance data security by providing a transparent and tamper-proof way to manage data.
4. Data-as-a-Service (DaaS)
DaaS will become more popular, allowing organizations to access and use data on demand without managing their own infrastructure.
5. Increased Focus on Data Privacy
With stricter data privacy regulations, organizations will need to invest more in data governance and security measures to protect sensitive information.
Conclusion
Services
Related posts
Why Atlassian Partners Play a Crucial Role in Atlassian Product Implementation
In today's fast-paced digital landscape, organizations are continually seeking tools that enhance collaboration, streamline workflows, and boost productivity....
Jira Service Management vs. Zendesk: A Comprehensive Comparison
Introduction In the era of digital-first business, having the right service management solution can make or break the customer and employee experience....
Smart Ways to Improve Team Productivity Through Workflow Optimization
In a world where digital transformation is reshaping how we work, workflow optimization has emerged as one of the most powerful levers to drive team...



