Table of Contents
Introduction
In complex product development—especially in regulated industries such as automotive, medical devices, aerospace, and industrial automation—organizations need a robust platform that unifies requirements management, design, development, testing, and compliance. codebeamer ALM (by Intland Software) is a comprehensive Application Lifecycle Management solution designed to manage the full lifecycle of products, from concept through release and maintenance.
This pillar page explains what codebeamer is, why it matters, and how organizations can apply it to achieve traceability, compliance, faster time-to-market, and higher product quality. You’ll find feature breakdowns, practical use cases, integration options, implementation guidance, migration considerations, ROI metrics, and best practices for scaling ALM across your organization.
What Is codebeamer ALM?
codebeamer ALM is an enterprise-grade application lifecycle management platform that supports collaborative product development and end-to-end traceability across requirements, risk, software, hardware, testing, and release management. It combines powerful features such as:
- Requirements engineering and traceability
- Risk & hazard analysis (FMEA, HARA)
- Workflow-driven change and configuration management
- Test management and automated test execution tracking
- DevOps integrations and CI/CD pipelines
- Audit trails and compliance management for standards (ISO 13485, ISO 26262, IEC 62304, DO-178C, etc.)
- Customizable processes and templates for regulated and non-regulated environments
Designed for both traditional V-model development and agile/DevOps practices, codebeamer enables cross-functional teams to collaborate while preserving governance and compliance.
Why codebeamer Matters
Modern product development combines software, electronics, and mechanical systems, all under increasing regulatory and market pressures. codebeamer ALM addresses these challenges by providing a connected, compliant, and efficient development environment. Below are ten key reasons why it matters:
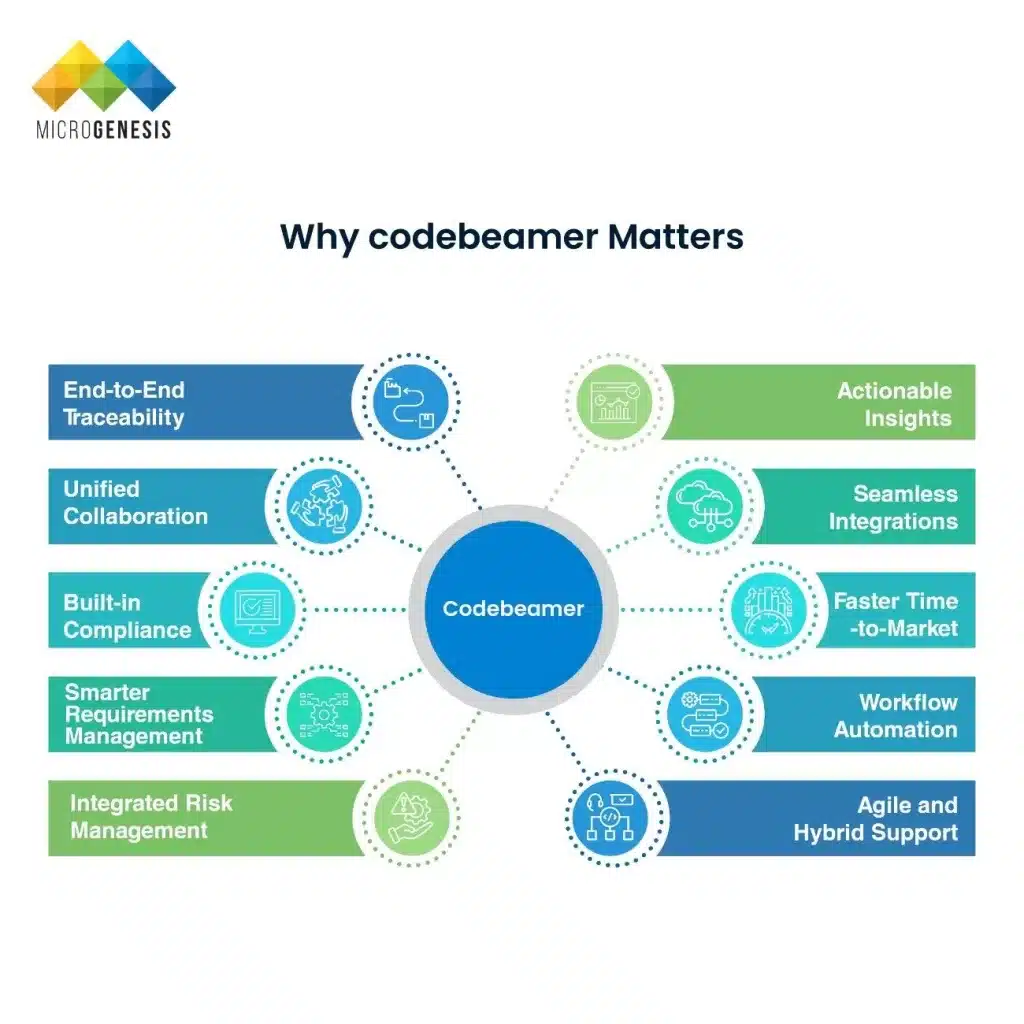
1.End-to-End Traceability
codebeamer links requirements, risks, development tasks, test cases, and releases in one environment, ensuring complete visibility and easy audit preparation.
2.Unified Collaboration
It centralizes communication across engineering, quality, and compliance teams, breaking down silos and improving coordination on complex projects.
3.Built-in Compliance
With templates and workflows for ISO 26262, IEC 62304, and other standards, codebeamer simplifies documentation and regulatory reporting.
4.Smarter Requirements Management
Teams can capture, review, and version requirements efficiently, linking them to implementation and testing for full verification coverage.
5.Integrated Risk Management
Features for FMEA, HARA, and safety analysis help teams identify, track, and mitigate risks early in the development cycle.
6. Agile and Hybrid Support
codebeamer accommodates both agile and V-model workflows, allowing flexibility without compromising traceability or governance.
7. Workflow Automation
Configurable workflows streamline approvals, status updates, and notifications, reducing manual work and improving consistency.
8. Faster Time-to-Market
Linked artifacts and automated impact analysis minimize rework and accelerate development cycles, enabling quicker releases.
9. Seamless Integrations
codebeamer connects with tools like Jira, Git, Jenkins, and Confluence, ensuring a unified and traceable toolchain.
10. Actionable Insights
Real-time dashboards and reports help teams monitor KPIs, track compliance, and continuously improve their development processes.
Core Features and Capabilities
Below is a structured breakdown of codebeamer’s primary capabilities and how they support product development lifecycles.

1.Requirements Management
- Capture, version, and review requirements with full audit trails.
- Support hierarchical requirements, attributes, and custom fields.
- Link requirements to test cases, design elements, and work items to maintain traceability.
2.Traceability and Impact Analysis
- Bidirectional, configurable trace links between requirements, risks, changes, tests, code, and releases.
- Impact analysis dashboards show downstream effects of changes to reduce regression and scope creep.
3.Risk & Safety Management
- Integrated modules for FMEA, HARA, and other risk analysis techniques.
- Map risks to requirements and tests to ensure mitigation measures are validated.
4.Test Management
- Plan, author, execute, and track test cases, manual or automated.
- Link test results to requirements and defects for full verification coverage.
5.Change & Configuration Management
- Workflow-driven change requests, approvals, and baselining.
- Branching and merging strategies for artifact versions.
- Support for controlled releases across hardware and software domains.
6.Agile and Hybrid Development
- Support Scrum, Kanban, SAFe, and hybrid processes.
- Backlog management, sprints, boards, and release planning integrated with ALM artifacts.
7.Collaboration and Review
- Collaborative review workflows, comments, and approvals.
- Role-based access and stakeholder-specific dashboards.
8.DevOps and CI/CD Integration
- Connect source control (Git, SVN), build servers (Jenkins, Bamboo), and test automation tools.
- Link commits and builds to requirements and tests for traceable continuous delivery.
9.Compliance Reporting and Auditability
- Pre-built and customizable report templates for regulatory evidence.
- Complete audit trails, electronic signatures, and trace matrices to support certifications.
10.Extensibility and Customization
- Tailor workflows, templates, fields, and process models to organizational requirements.
- REST APIs and plugin architecture for custom integrations.
Key Benefits by Stakeholder
For Product Managers
- Single source of truth for requirements and priorities.
- Better visibility into progress, risks, and release readiness.
For Systems & Safety Engineers
- Integrated risk analysis and traceability to validate mitigations.
- Support for standards-driven processes and evidence collection.
For Development Teams
- Clear linkage between requirements, code, and tests.
- Reduced rework through early impact analysis.
For QA & Test Engineers
- Centralized test case management and execution tracking.
- Automated traceability of test coverage to requirements.
For Compliance & Auditors
- Ready access to trace matrices, audit trails, and signed approvals.
- Simplifies demonstration of compliance during assessments.
Typical Use Cases
Automotive (ISO 26262)
Manage system, software, and safety requirements; conduct HARA and FMEA; maintain traceability required for functional safety certification.
Medical Devices (ISO 13485 / IEC 62304)
Ensure design controls, validate software against requirements, track clinical feedback and post-market changes with compliant documentation.
Aerospace & Defense (DO-178C / DO-254)
Implement strict configuration management, traceability, and verification planning for high-assurance systems.
Industrial Automation
Coordinate multi-disciplinary development of PLCs, embedded controllers, and supervisory systems with system-level traceability.
Enterprise Software & Hardware Products
Large-scale product development requiring integration of agile teams with regulated engineering practices.
How codebeamer Fits into Modern Development Practices
Agile at Scale
codebeamer supports agile practices (backlog management, sprints, boards) while preserving traceability and governance. This enables enterprises to adopt agile methodologies without losing evidence required for compliance.
V-Model and Waterfall
For organizations requiring plan-driven models, codebeamer’s structured workflows, approvals, and baselining support V-model development with clear verification and validation steps.
DevSecOps
Embedding security and test automation into the pipeline is enabled by codebeamer’s DevOps integrations, enabling teams to link security scans and automated test runs to requirements and issues.
Integrations and Ecosystem
codebeamer integrates with common development and collaboration tools to create a connected toolchain:
- Version Control: Git, SVN, Perforce
- CI/CD: Jenkins, Bamboo, GitLab CI, Azure DevOps
- IDE & Code: Integration points for traceability to commits and code branches
- Testing Tools: Selenium, Robot Framework, Test automation frameworks via connectors
- ALM & PLM: Integrations with Enterprise tools (e.g., Jira, IBM DOORS, PTC Windchill) for cross-platform workflows
- Collaboration: Confluence, Slack, Microsoft Teams
- Data & Analytics: BI and reporting tools via APIs
These integrations let teams maintain traceability across the entire toolchain and automate artifact synchronization.
Implementation & Adoption Guide
A successful codebeamer implementation balances technical configuration with organizational change management. Below is a practical roadmap.
Assessment & Planning
- Conduct a readiness assessment: maturity of processes, stakeholders, compliance needs.
- Define scope: projects, teams, and processes to onboard first.
- Identify success metrics: traceability coverage, cycle time reduction, audit readiness.
Process Design
- Map current workflows and define target processes (agile, V-model, hybrid).
- Design object model (requirements, tests, risks, work items) and link rules.
- Establish naming conventions, field definitions, and permission schemas.
Configuration & Integration
- Configure artifacts, workflows, and templates.
- Set up integrations with source control, CI, testing tools, and documentation systems.
- Implement automated reporting and trace matrices.
Pilot & Validate
- Pilot with a single product or development stream.
- Validate traceability, approvals, and report generation.
- Collect user feedback and refine configurations.
Rollout & Training
- Gradually expand to more teams with role-based training.
- Provide playbooks, templates, and a Center of Excellence (CoE) for governance.
Continuous Improvement
- Monitor KPIs and adjust processes.
- Conduct regular audits of field usage, link completeness, and automation rules.
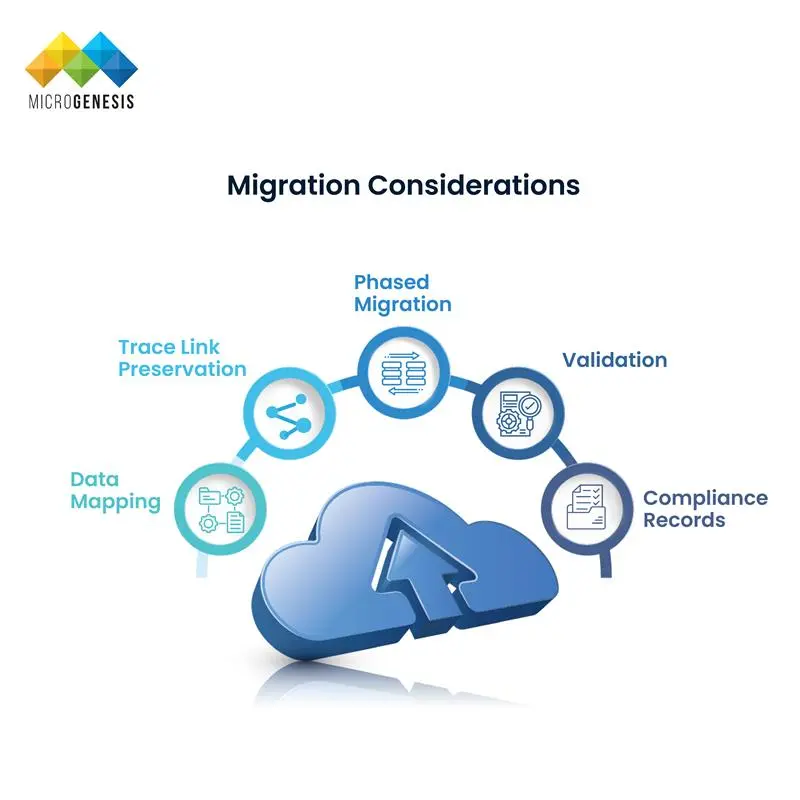
Migration Considerations
Many organizations migrate from spreadsheets, legacy ALM tools, or fragmented systems. Common migration considerations include:
- Data Mapping: Map legacy artifact types, fields, and relationships to codebeamer’s object model.
- Trace Link Preservation: Preserve historic trace links where possible for audit continuity.
- Phased Migration: Start with requirements and tests, then move changes and code links.
- Validation: Verify migrated data with stakeholders to ensure accuracy.
- Compliance Records: Maintain exportable records for regulatory audits during and after migration.
Working with experienced implementation partners or vendor professional services can mitigate migration risk.
Measuring Success & ROI
Quantifying the impact of codebeamer helps secure executive buy-in. Typical ROI indicators include:
- Time-to-market reduction: Faster approvals and fewer rework cycles accelerate releases.
- Fewer defects post-release: Better traceability and test coverage reduce escaped defects.
- Audit cycle reduction: Pre-built reports and trace matrices shorten audit preparation.
- Reduced rework: Impact analysis prevents costly design changes late in the cycle.
- Process efficiency: Automated workflows and templates save hours per release.
Define baseline metrics before adoption (e.g., average defect density, audit prep time) and track improvements post-implementation.
Security, Governance & Compliance
In today’s regulatory landscape, organizations must ensure that every stage of the product lifecycle — from requirements definition to release — adheres to strict security and governance standards. This is especially critical for industries such as automotive, medical devices, aerospace, and defense, where compliance and product safety are non-negotiable.
codebeamer ALM is designed with enterprise-grade security, auditability, and compliance features that safeguard sensitive product data while maintaining agility and collaboration. It bridges the gap between regulatory rigor and modern development practices.
1. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and Fine-Grained Permissions
codebeamer provides a robust RBAC framework, enabling administrators to control who can access, modify, or approve specific artifacts.
Permissions can be defined at multiple levels — project, tracker, or item — ensuring that users see and interact only with information relevant to their role.
This fine-grained control minimizes human error, protects intellectual property, and enforces process discipline across large, distributed teams.
2. Complete Audit Trails
Every action within codebeamer — whether it’s a requirement update, workflow transition, or approval — is automatically logged in an immutable audit trail.
These detailed histories capture who did what, when, and why, providing verifiable evidence for internal reviews and external audits.
This not only supports compliance with regulatory frameworks but also enhances accountability and transparency across the organization.
3.Electronic Signatures and Approval Workflows
For industries operating under standards like FDA 21 CFR Part 11 or ISO 13485, electronic signatures are essential to validate changes and approvals.
codebeamer enables configurable e-signature workflows, ensuring that each sign-off is securely recorded, time-stamped, and traceable.
These workflows support hierarchical approval structures, reducing manual paperwork while maintaining legal and regulatory compliance.
4.Data Residency and Deployment Flexibility
Data sovereignty and security are vital, particularly for organizations handling sensitive product or customer information.
codebeamer offers flexible deployment options — including on-premises, private cloud, and public cloud — allowing organizations to meet their unique data residency, compliance, and IT governance requirements.
For defense, healthcare, or government sectors, on-premises deployment ensures maximum control over infrastructure and access.
5.Compliance-Centric Framework
Beyond individual features, codebeamer provides an end-to-end compliance framework.
Predefined templates and workflows support major standards such as ISO 26262 (automotive safety), IEC 62304 (medical software), DO-178C (aerospace), and ASPICE (software process improvement).
By integrating compliance into daily development activities, organizations can ensure that all deliverables meet industry regulations without introducing unnecessary overhead.
6.Secure Collaboration and Change Management
codebeamer balances secure governance with open collaboration.
Teams can collaborate through discussions and reviews without compromising data security. Every change request or modification goes through controlled workflows, maintaining both agility and traceability.
7.Data Integrity and Version Control
All artifacts in codebeamer are version-controlled, ensuring a permanent record of every revision.
Version history, baselining, and controlled approvals maintain the integrity and reproducibility of design data — crucial for regulated audits and long product lifecycles.
Best Practices for Scaling ALM with codebeamer
Scaling Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) across an enterprise requires structure, governance, and continuous improvement. As organizations grow, maintaining alignment and compliance across distributed teams becomes critical. The following best practices ensure a successful, sustainable rollout of codebeamer ALM.
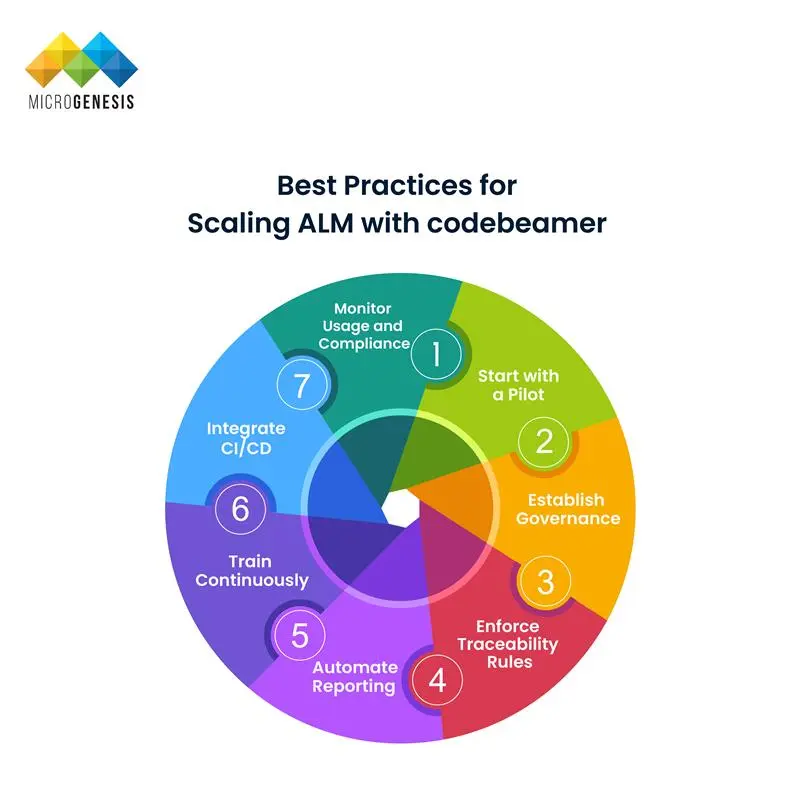
1. Start with a Pilot
Begin with a small, representative project to validate workflows, traceability rules, and integrations before enterprise adoption.
A pilot helps identify configuration gaps, collect feedback, and refine processes, reducing risk during full deployment. Once validated, replicate successful patterns across other business units.
2. Establish Governance
Create an ALM Center of Excellence (CoE) to manage process templates, workflows, and data standards.
Governance ensures consistency, accountability, and compliance across teams while maintaining flexibility for project-specific customization.
3. Enforce Traceability Rules
Define clear traceability policies linking requirements → risks → tests → defects.
Mandatory link enforcement guarantees coverage, supports impact analysis, and ensures teams can provide auditable evidence for regulatory compliance.
4. Automate Reporting
Set up predefined dashboards and automated reports for stakeholders, quality teams, and auditors.
Automating compliance and progress reports minimizes manual effort, improves accuracy, and ensures stakeholders always have real-time visibility into development status.
5. Train Continuously
Provide ongoing, role-based training and accessible documentation to onboard new users efficiently.
Regular workshops, learning modules, and user feedback sessions help maintain process adherence and promote user confidence across departments.
6. Integrate CI/CD
Connect codebeamer with build servers, test automation frameworks, and source control systems.
Integrating CI/CD pipelines ensures that every commit, build, and test execution remains traceable to its originating requirement, enhancing both transparency and accountability.
7. Monitor Usage and Compliance
Leverage dashboards and analytics to track usage, field completion, and adherence to workflows.
Regular audits help identify process deviations, measure adoption rates, and continuously optimize performance across teams and projects.
Comparing codebeamer with Alternatives
Choosing the right Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) platform requires evaluating tools across multiple dimensions — from traceability and compliance to scalability and integration flexibility. Each organization’s priorities may vary based on industry regulations, development models, and existing toolchains. The following criteria outline key aspects to consider when comparing codebeamer with other ALM solutions such as Jira Align, Polarion ALM, IBM Engineering Lifecycle Management (ELM), and Helix ALM.
1. Traceability Depth
Evaluate how comprehensively a platform connects requirements, risks, test cases, and code artifacts.
codebeamer offers bidirectional, end-to-end traceability, enabling impact analysis across all lifecycle stages — a key advantage for regulated and safety-critical projects. This feature ensures that every change or defect can be traced back to its originating requirement.
2. Regulatory and Compliance Support
For industries governed by strict standards like ISO 26262, IEC 62304, DO-178C, or FDA 21 CFR Part 11, compliance capabilities are non-negotiable.
codebeamer includes built-in templates, electronic signatures, and audit trails tailored to these standards, reducing the manual burden of preparing documentation and audit evidence.
3. Flexibility and Customization
Different teams require different workflows and data structures.
codebeamer’s flexible object model allows organizations to customize artifacts, workflows, and approval processes without extensive development effort. This adaptability supports both agile and V-model methodologies, making it ideal for hybrid enterprises.
4. Integration Capabilities
Modern development depends on toolchain interoperability.
codebeamer integrates natively with CI/CD tools (e.g., Jenkins, GitLab), version control systems (e.g., Git, SVN), test management suites, and collaboration platforms such as Confluence and Microsoft Teams.
These integrations create a unified digital thread across software, hardware, and quality management systems.
5. Scalability and Performance
Enterprise-level product development often involves thousands of artifacts and distributed teams.
codebeamer is engineered to scale efficiently, offering reliable performance for large datasets, multi-site deployments, and parallel development projects without compromising system responsiveness.
6. Deployment Options
Different organizations have varying IT and data security requirements.
codebeamer provides multiple deployment models — cloud, private cloud, and on-premises — giving enterprises control over data residency, compliance, and infrastructure preferences.
7. Collaboration and Visibility
Effective ALM tools should promote transparency across functions.
codebeamer provides customizable dashboards, real-time metrics, and stakeholder views, ensuring that engineering, compliance, and management teams have synchronized visibility throughout the lifecycle.
8. Cost Efficiency and ROI
While some ALM tools require extensive configuration or external add-ons, codebeamer’s built-in compliance and risk modules reduce total cost of ownership.
Its automation and reporting capabilities also save significant time during audits and release cycles, delivering measurable ROI.
Common Implementation Pitfalls & How to Avoid Them

- Over-Customization: Deep customizations can complicate upgrades. Prefer configuration over heavy customization.
- Skipping Training: Underestimating training leads to poor adoption. Invest in onboarding and playbooks.
- Ignoring Governance: Without governance, inconsistent practices can erode traceability. Establish a CoE early.
- Rushing Migration: Migrate in phases and validate data integrity to avoid disruptions.
Future Trends & Roadmap Considerations
ALM platforms are evolving along with software development trends. Key areas to watch:
- Increased DevOps and pipeline integration for continuous traceability.
- AI-assisted analytics for impact analysis, risk detection, and requirements quality assessment.
- Model-based systems engineering (MBSE) integrations for complex cyber-physical systems.
- Enhanced collaboration features and low-code customization for broader stakeholder adoption.
Evaluate vendor roadmaps and community ecosystems to ensure alignment with your long-term strategy.
Conclusion
For organizations building complex, regulated, or safety-critical products, a robust ALM platform like codebeamer delivers the discipline needed to align strategy, engineering, and compliance. By centralizing requirements, risk analysis, testing, and development artifacts—and by providing end-to-end traceability—codebeamer helps teams reduce rework, accelerate delivery, and streamline audits.
Successful adoption depends on careful process design, phased implementation, governance, and continuous improvement. When paired with appropriate integrations and training, codebeamer becomes a strategic platform that supports innovation while maintaining the rigor required in regulated industries.
Bitbucket isn’t just about storing code
it’s about building smarter, faster, and more collaborative software delivery pipelines.
Our Blogs












