Table of Contents
Introduction
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is one of the most transformative technologies in enterprise IT today. By automating repetitive, rule-based tasks, RPA enables organizations to reduce costs, improve accuracy, and boost employee productivity.
As industries across the globe push toward digital transformation, RPA is becoming a critical enabler of efficiency and innovation. This pillar guide explores RPA in depth — from its definition and benefits to real-world use cases, implementation strategies, challenges, and future trends.
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a technology that uses software robots (often called bots) to automate routine, repetitive, and rule-based business tasks that would normally require human intervention. These bots don’t exist physically like industrial robots; instead, they are virtual agents that work inside digital environments, interacting with applications, systems, and data much like a human user would.
In practical terms, RPA bots can log into systems, enter data, extract information, move files, send emails, and even trigger responses across multiple applications. What makes RPA powerful is its ability to perform these tasks faster, more accurately, and around the clock without fatigue or error.
Key Characteristics of RPA
- Non-invasive – Unlike traditional automation that often requires deep system changes, RPA sits on top of existing applications. It works through user interfaces and APIs, meaning organizations don’t need to rebuild or replace legacy systems.
- Rule-driven – Bots follow a set of pre-defined rules and instructions. If a process has a clear structure (e.g., invoice data entry), it’s a perfect candidate for RPA.
- Scalable – RPA is not limited to a single workflow. Businesses can deploy thousands of bots across functions, scaling automation as demand grows.
- Flexible – RPA is industry-agnostic. From finance and HR to healthcare and retail, bots can be tailored to automate processes across any department or domain.
Why RPA is Often the First Step in Automation
Many organizations choose RPA as their entry point into digital transformation because it provides quick wins with minimal disruption. Unlike large-scale IT overhauls, RPA works with existing tools and processes. That means:
- Businesses see rapid ROI (return on investment), often within months.
- Employees can offload mundane, repetitive work and focus on more strategic, value-driven activities.
- RPA builds the foundation for more advanced automation — such as Intelligent Automation (IA) or Hyperautomation — by showing the potential of blending automation with AI and analytics.
In essence, RPA bridges the gap between current manual operations and a fully automated future, making it a critical first step in modernizing business processes.
Why RPA Matters Today
In today’s hyper-competitive and digital-first business environment, organizations are under relentless pressure to deliver faster, reduce costs, and enhance customer experiences — all while navigating tighter compliance and limited resources. Traditional manual processes simply cannot keep up with these demands. They are often:
- Time-consuming – Employees spend hours on data entry, reconciliations, or repetitive administrative work.
- Error-prone – Even the most skilled workers make mistakes, especially under pressure or with monotonous tasks.
- Costly – Maintaining manual operations across large enterprises drives up labor costs and slows business growth.
- Rigid – Human-dependent workflows struggle to scale as business needs change.
How RPA Solves These Challenges
RPA provides a direct solution by transforming manual operations into automated, scalable, and error-free digital workflows. Specifically, it helps organizations:
- Automate repetitive tasks – Offload mundane work (e.g., invoice processing, payroll, or report generation) to bots, allowing employees to focus on innovation and problem-solving.
- Reduce operational costs – Bots work faster than humans, operate 24/7, and require minimal supervision, reducing labor costs and boosting efficiency.
- Enhance compliance – Every RPA bot executes processes based on strict rules and logs every action, ensuring full traceability and adherence to regulatory requirements.
- Support digital transformation – Without requiring costly system overhauls, RPA integrates seamlessly with legacy and modern applications, helping organizations transform step by step.

The Market Momentum
The significance of RPA is reflected in its growth. According to Gartner, the RPA market is expanding at more than 20% annually, making it one of the fastest-growing enterprise software segments globally. This rapid adoption is fueled by organizations recognizing RPA not just as a cost-saving tool, but as a strategic enabler of agility, innovation, and competitive advantage.
How RPA Works: The Basics
At its core, RPA is about mimicking human actions in digital systems. Think of it as a virtual workforce that can perform the same clicks, keystrokes, and navigations that a person would do — but with greater speed, accuracy, and consistency.
The Typical RPA Workflow
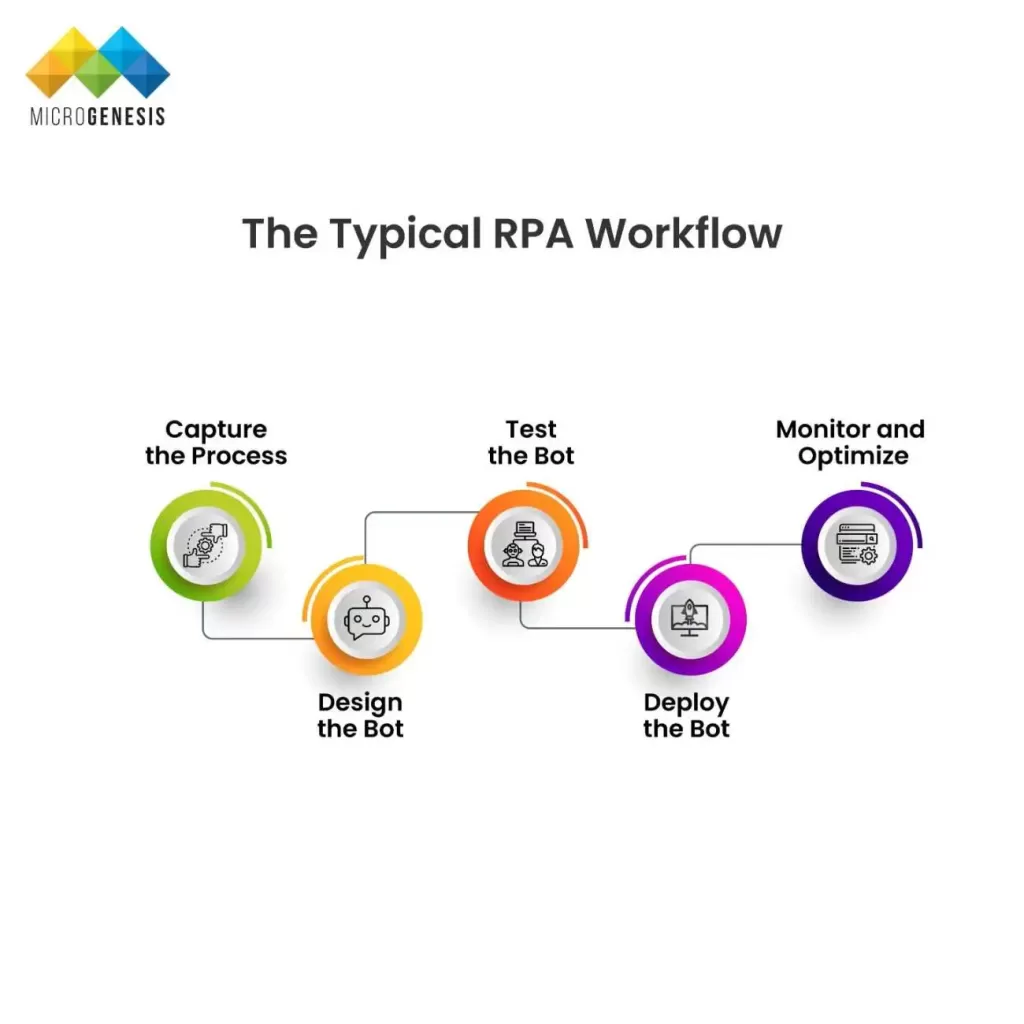
RPA implementation generally follows a structured cycle:
- Capture the Process – Identify repetitive, rule-based, and high-volume tasks that are prime candidates for automation (e.g., claims processing, order entry, compliance checks).
- Design the Bot – Using RPA platforms (such as UiPath, Automation Anywhere, or Blue Prism), developers or business analysts design automation scripts. Many modern platforms use low-code or no-code interfaces, making bot design accessible to non-technical staff.
- Test the Bot – Bots are tested in controlled environments to validate accuracy, stability, and exception handling before going live.
- Deploy the Bot – Once verified, bots are moved into production environments where they execute tasks alongside human workers.
- Monitor and Optimize – After deployment, performance is tracked continuously. Organizations refine workflows, add new capabilities, and scale automation to other areas.
- This cycle ensures RPA delivers sustained business value instead of being a one-off implementation.
Technologies Behind RPA
Several technologies make RPA effective and versatile:
- Screen scraping – Enables bots to extract information from user interfaces, even in legacy systems that lack APIs.
- API integrations – Allow bots to directly communicate with modern applications, ensuring seamless and secure data exchange.
- Machine learning (in Intelligent Automation) – Extends RPA with cognitive capabilities, enabling bots to handle semi-structured or unstructured data such as emails, invoices, or documents.
- Workflow orchestration – Ensures multiple bots and processes work together efficiently, often across different systems and departments.
By combining these technologies, RPA not only automates basic tasks but also forms the foundation for hyperautomation, where advanced AI, analytics, and orchestration create truly intelligent enterprises.
Benefits of RPA
One of the reasons Robotic Process Automation has gained such rapid adoption is its tangible business impact. Unlike some digital transformation initiatives that take years to pay off, RPA delivers measurable benefits within months of implementation.

1. Cost Reduction
Labor costs are among the highest operational expenses for most organizations. By automating routine, rule-based work, RPA can reduce reliance on manual labor for repetitive tasks. This doesn’t necessarily mean replacing employees — instead, it allows companies to reallocate their workforce to more strategic and customer-focused activities. For large enterprises, this can translate into millions of dollars saved annually while also improving agility.
2. Productivity Boost
Unlike humans, RPA bots can operate 24/7, 365 days a year without breaks, vacations, or downtime. This continuous operation dramatically improves throughput, enabling organizations to handle higher volumes of work without scaling headcount. For example, processes like payroll, invoice processing, or claims validation that once took days can now be completed in hours.
3. Improved Accuracy
Human errors are unavoidable in repetitive work, especially when employees are under time pressure or handling large volumes of data. RPA eliminates this issue by performing tasks with perfect consistency. From data entry to calculations, bots ensure accuracy and reduce the costly rework that often results from mistakes.
4. Compliance and Auditability
Regulated industries such as finance, healthcare, and pharmaceuticals face strict compliance requirements. RPA strengthens compliance by ensuring that every process follows predefined rules and workflows. Additionally, every bot action is logged automatically, creating a digital audit trail that makes regulatory reporting and audits faster, easier, and less stressful.
5. Employee Satisfaction
While some fear that automation replaces jobs, the reality is that RPA often improves employee satisfaction. By handling the repetitive and mundane tasks, bots allow employees to focus on higher-value, creative, and strategic work. This not only boosts morale but also helps attract and retain top talent who prefer engaging and meaningful roles over monotonous work.
Common RPA Use Cases
RPA’s flexibility makes it applicable across industries and functions. Any process that is repetitive, rule-based, and high-volume is a candidate for automation. Below are some of the most common and impactful applications:

Finance & Accounting
Finance teams handle some of the most repetitive yet critical business functions. RPA helps:
- Invoice processing – Automating invoice capture, validation, and posting into ERP systems.
- Reconciliation – Matching transactions across multiple systems with speed and accuracy.
- Payroll management – Automating payroll calculations, approvals, and disbursements.
The result is faster processing, fewer errors, and stronger compliance.
Human Resources (HR)
RPA supports HR departments by streamlining employee-related processes:
- Employee onboarding – Automating account creation, document collection, and training enrollment.
- Benefits administration – Handling enrollment updates, claims, and changes with minimal human effort.
- Timesheet validation – Ensuring accurate attendance and working hours without manual checks.
This not only saves HR teams time but also improves the employee experience from day one.
Customer Service
Customer-facing teams often struggle with repetitive tasks that delay response times. RPA helps by:
- Automating responses to FAQs – Reducing workload by integrating bots with chat systems.
- Processing customer requests – Handling routine updates such as address changes or order tracking.
- Updating CRM systems – Automatically logging customer interactions for a single source of truth.
This enables faster response times, happier customers, and more efficient service teams.
IT Operations
IT teams face increasing demands for support and infrastructure management. RPA improves IT efficiency with:
- Automated monitoring – Bots detect anomalies and trigger alerts in real-time.
- Password resets – Automating one of the most common IT helpdesk requests.
- Incident management – Logging, categorizing, and escalating incidents to the right teams.
This frees IT teams to focus on strategic projects like cloud migration or cybersecurity.
Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, accuracy and compliance are paramount. RPA supports by:
- Claims processing – Automating insurance claims to reduce approval times and minimize fraud.
- Patient data management – Ensuring accurate and timely updates to patient records across systems.
- Regulatory reporting – Generating compliance reports automatically to meet strict healthcare regulations.
By reducing administrative burdens, RPA allows healthcare professionals to spend more time on patient care, ultimately improving outcomes.
RPA vs. Traditional Automation
Although both RPA and traditional automation aim to improve efficiency, the approach and flexibility are very different.
- Traditional Automation requires integration at the system or code level. This often involves rewriting applications, changing backend logic, or modifying databases. While powerful, it’s expensive, invasive, and time-consuming — making it impractical for organizations with complex, legacy environments.
- Robotic Process Automation, on the other hand, works at the user interface level. Bots interact with software the same way a human user would — by clicking, typing, or navigating screens. This makes RPA much faster to deploy, less disruptive, and easier to scale across multiple applications.
RPA is also far more flexible, since it doesn’t require organizations to rebuild existing systems. This makes it ideal for enterprises with legacy IT ecosystems, where replacing core systems isn’t feasible in the short term.
The RPA Implementation Lifecycle
For RPA to deliver measurable ROI, organizations must approach implementation with a structured lifecycle.
Process Assessment
Not all workflows are suitable for automation. The first step is identifying processes that are:
- Repetitive and rule-based.
- High-volume with low variability.
- Critical to business outcomes but prone to human error.
Proof of Concept (PoC)
Instead of automating everything at once, organizations should start small. A PoC helps validate whether RPA can deliver value in a specific use case, build stakeholder confidence, and uncover technical limitations before scaling.
Bot Development
Using platforms like UiPath, Automation Anywhere, or Blue Prism, developers (or even business analysts with low-code tools) create the automation scripts. This stage involves defining workflows, exception handling, and integration points.
Testing & Deployment
Before bots are rolled out, they must be tested in sandbox environments to validate performance, accuracy, and reliability. Once approved, they are deployed into production environments where they execute processes in real-world conditions.
Monitoring & Maintenance
Automation is never “set and forget.” Continuous monitoring ensures bots are functioning properly, while updates and optimizations help adapt to changing business rules or system updates.
RPA Tools and Technologies
The RPA market is filled with powerful platforms. Choosing the right one depends on your industry, goals, and IT environment.
- UiPath – Known for its user-friendly interface and large community, making it great for enterprises just starting out.
- Automation Anywhere – Offers robust cloud-native capabilities, making it ideal for enterprises scaling automation in hybrid environments.
- Blue Prism – Favored by large organizations for its enterprise-grade governance, scalability, and security features.
- Microsoft Power Automate – A strong choice for businesses already invested in the Microsoft ecosystem, with seamless Office 365 integration.
- Pega Systems – Combines RPA with Business Process Management (BPM), enabling more complex, end-to-end automation.
When evaluating RPA tools, businesses should consider:
- Scalability – Can it handle thousands of bots and transactions?
- Security – Does it comply with enterprise security and data privacy standards?
- Integration – Does it work with both legacy and modern applications?
- Ease of Use – Can business users design bots without heavy IT involvement?
Challenges in RPA Implementation
While RPA delivers enormous value, organizations must prepare for challenges:
- Process Complexity – Not all workflows are suitable; highly judgment-based tasks may fail with RPA.
- Scalability Issues – Many organizations succeed with pilots but struggle to scale bots enterprise-wide.
- Change Management – Employees may fear job losses, leading to resistance.
- Maintenance Overhead – Bots can “break” if application UIs or business rules change.
- Skill Gaps – Lack of trained RPA developers and governance experts can slow adoption.
By acknowledging these challenges early, businesses can develop mitigation strategies such as training, governance frameworks, and phased rollouts.
Best Practices for RPA Success
To maximize ROI, organizations should adopt the following practices:
- Start Small, Scale Fast – Use PoCs to build momentum, then expand into enterprise-wide deployments.
- Involve Business and IT – Ensure cross-functional collaboration for both process expertise and technical implementation.
- Prioritize Governance – Define policies for bot lifecycle management, compliance, and monitoring.
- Automate Incrementally – Focus first on high-volume, high-impact processes before tackling complex workflows.
- Train and Upskill Employees – Empower teams to collaborate with bots and use freed-up time for innovation.
These practices ensure RPA delivers sustainable value, not just short-term wins.
Intelligent Automation: RPA + AI
RPA solutions are powerful on their own, but when combined with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML), they evolve into Intelligent Automation (IA). IA allows organizations to automate not just rule-based tasks but also processes requiring decision-making, data interpretation, and pattern recognition.
Examples of Intelligent Automation:
- Chatbots + RPA – Customer service bots can answer FAQs and trigger backend processes automatically.
- Fraud detection – AI models analyze transactions for suspicious behavior, while RPA bots act on flagged cases.
- Document processing – Combining OCR (Optical Character Recognition) with RPA to extract data from invoices, contracts, or handwritten forms.
This is the future of enterprise automation, where RPA and AI work together to deliver end-to-end, intelligent workflows.
RPA in Different Industries
RPA is industry-agnostic, but its impact is particularly strong in:
- Banking & Finance – Automates KYC verification, compliance reporting, and fraud detection.
- Healthcare – Streamlines claims processing, billing, and patient record updates.
- Manufacturing – Optimizes supply chain management, procurement, and inventory tracking.
- Retail – Automates order fulfillment, loyalty program updates, and pricing adjustments.
- Public Sector – Reduces administrative overhead in licensing, permits, and benefits administration.
Each industry benefits from faster operations, higher compliance, and improved service delivery.
Future of RPA
The RPA landscape is evolving rapidly. Key future trends include:
- Hyperautomation – Combining RPA, AI, ML, and BPM to create fully automated, intelligent processes.
- Cloud-Native RPA – Shifting bots to the cloud for better scalability and flexibility.
- Citizen Development – Empowering non-technical employees to design bots using low-code/no-code platforms.
- End-to-End Automation – Moving beyond task automation to automate entire business processes.
In the coming years, RPA will no longer be viewed as just a cost-saving tool but as a strategic enabler of enterprise agility and resilience.
Conclusion: RPA as a Strategic Enabler
Robotic Process Automation is not just another IT tool — it is a strategic capability that enables organizations to transform the way they operate. By automating repetitive tasks, businesses can reduce costs, enhance compliance, and empower employees to focus on value-driven activities.
At MicroGenesis, we help enterprises design, implement, and scale RPA solutions that align with their business goals. From process assessment and bot development to governance and managed services, our experts ensure your RPA journey is seamless, secure, and future-ready.
RPA is not just about doing things faster — it’s about building an agile, resilient enterprise prepared for tomorrow’s challenges.
Get Started Today!
Fill out the form below, and our team will reach out to help you optimize your IT infrastructure and ensure enterprise-wide transformation.
Our Blogs












