Are you tired of looking for the right tool for your project management? Atlassian Jira has emerged as one of the most flexible and powerful platforms for...

Ultimate Guide to DevOps
What Is DevOps?
BROWSE TOPICS
Understanding DevOps
DevOps is that silent hero bridging the gap between speedy development of innovative products and IT operations to ensure that the business wins every time. It’s not just a buzzword, but is rather a transformative approach that is reshaping how we build and deliver software. In fact, according to research by Global Markets Insight, the DevOps market is expected to expand by 20% CAGR from 2023 to 2032 to be worth more than $70 billion. This demand is driven by the urgent requirement to reduce the time taken to develop software and the time-to-market.
In the application release process at IT firms, the development department is primarily responsible for designing, coding, and building the applications. And, the operations department manages servers, ensures security, oversees scaling, and maintains backups within the business system. DevOps software development method integrates and streamlines development (Dev) and operations (Ops) workflows to improve collaboration and productivity.
In this article, we’ll learn the A-Zs of DevOps and understand why engaging with a devops service provider will benefit your business.. Read on to know about the best practices and how you can leverage DevOps principles in the best way possible.
The DevOps Culture

The DevOps concept eliminates issues that arise during the development process. Its primary purpose is to make the entire process less hectic.
DevOps is not just a set of practices; it’s a cultural shift that DevOps services companies and organisations involved with devops consulting services need to embark on. This isn’t an easy task. According to a survey report by Markets and Markets, 84% of the respondents have reported facing challenges in DevOps implementation. That, however, only goes on to establish the importance being laid on DevOps services and DevOps culture.
To understand its culture better, we must know how it functions. It promotes a collaborative environment where developers and operations teams share responsibilities and insights. This culture of shared responsibility and transparency leads to better problem-solving and innovation.
Key elements of DevOps culture include:
- Collaboration: Development, operations, and other stakeholders work together throughout the DevOps software lifecycle (DevOps SDLC).
- Ownership: Teams are responsible for the entire application lifecycle, from development to deployment.
- Quality of product: increases
- Continuous Improvement: Teams constantly seek ways to improve processes, tools, and collaboration.
DevOps culture is all about fostering collaboration and communication across teams. Instead of working in isolated silos, teams come together to share responsibilities and insights. This cultural shift promotes a more holistic approach to software development and operations, where everyone works towards a common goal: delivering value to the customer.
DevOps Practices and Methodologies

Companies rely on DevOps to keep things running smoothly like a well-oiled machine. All companies aspire that their development and operations departments work harmoniously, understanding the importance of that collaboration to reduce time-to-market. DevOps brings that dream into reality. DevOps creates a continuous cycle that spans from end to end, enabling companies to ensure that they execute each product development and deployment phase efficiently and effectively. Gartner predicts that 80% of software engineering firms will establish platform teams by 2026 to achieve exactly this.
Learn more about Why DevOps is Essential for Enterprise Business Success.
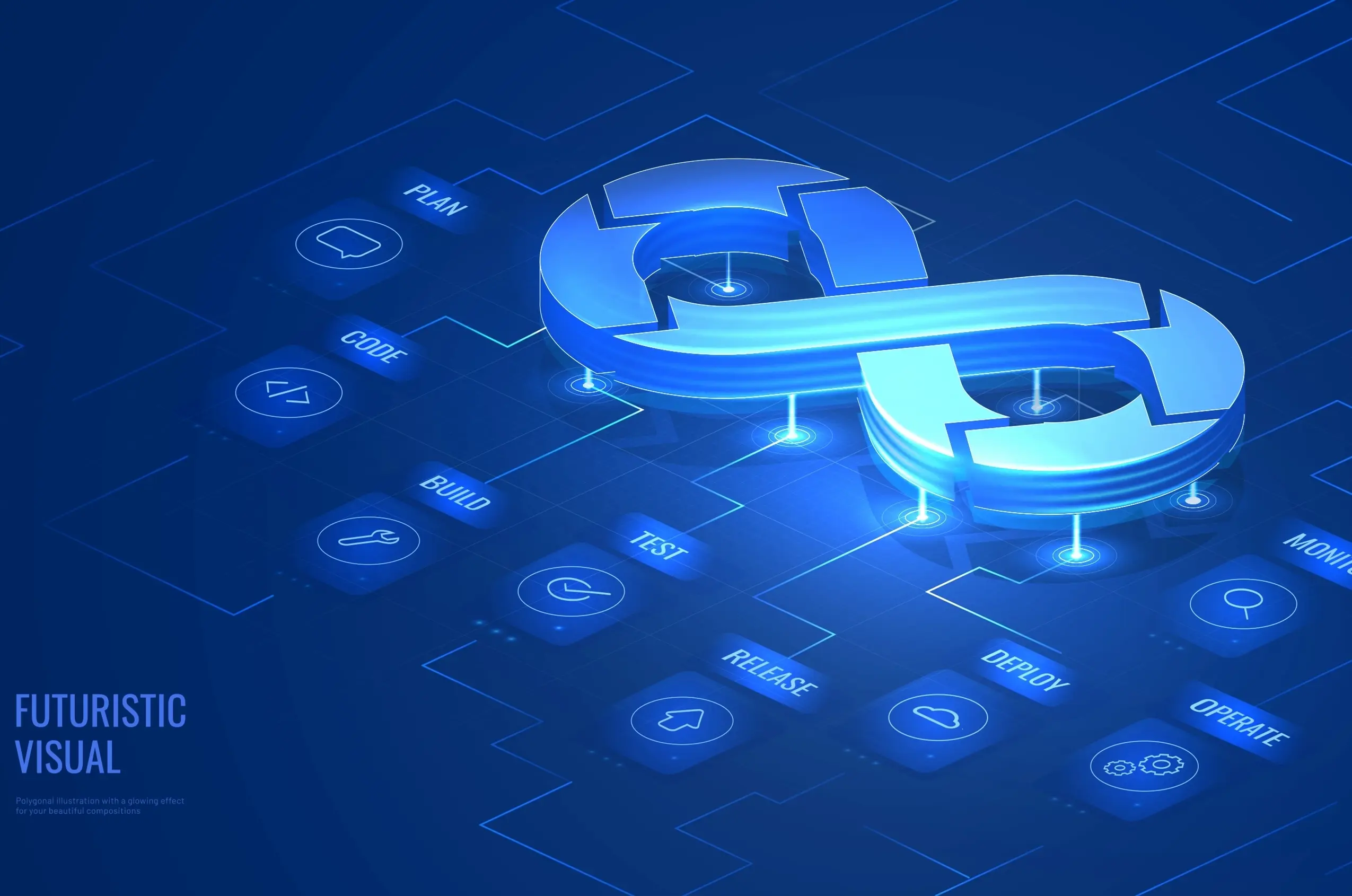
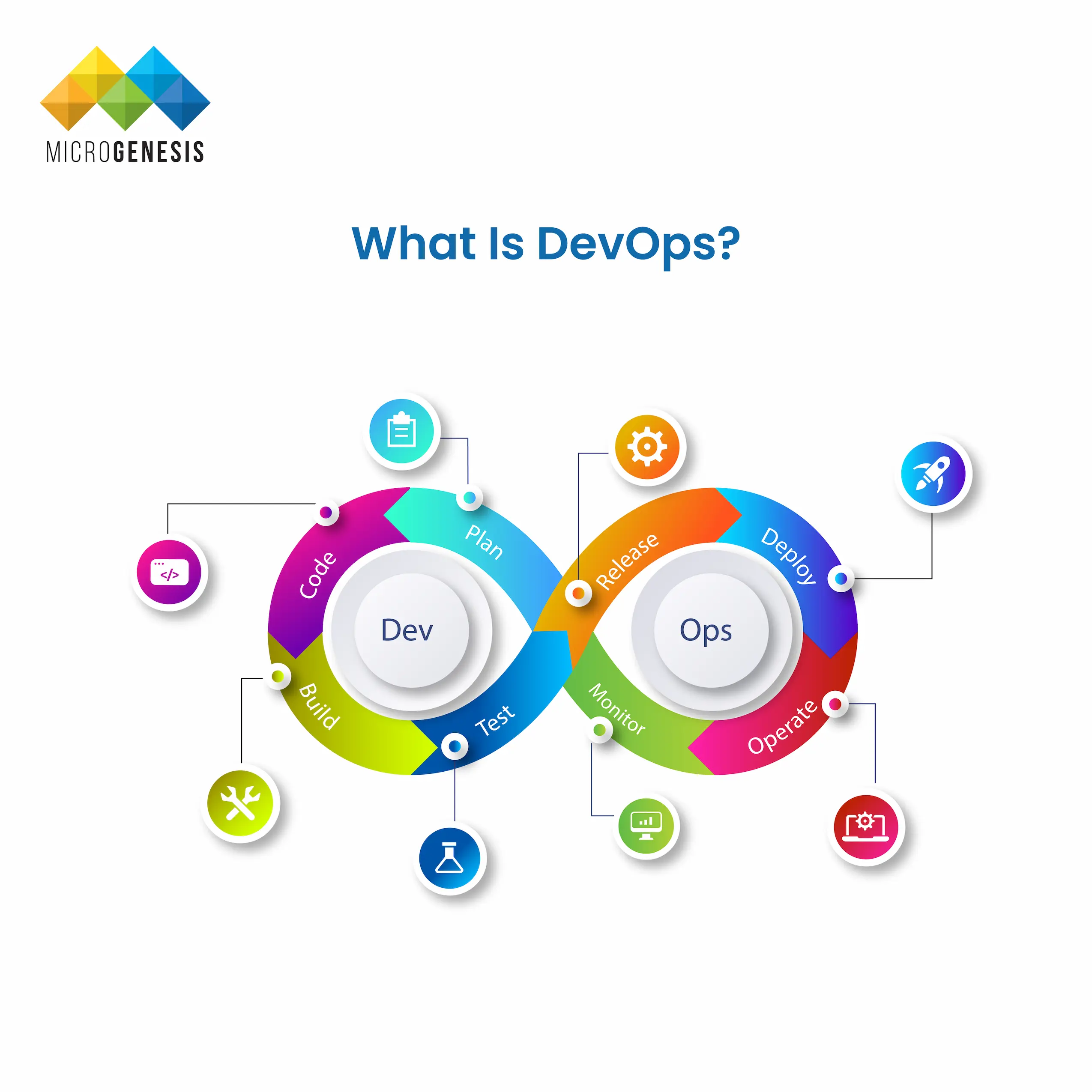
- Plan: This is the initial and perhaps the most important phase, where teams determine what needs to be built. Planning involves gathering all the requirements, setting goals, and defining the features and functionalities of the final product.
- Code In the next phase, developers write the code to build the final product. This phase involves creating the software’s architecture and developing the necessary features and functionalities.
- Build Once the developers write the code, they compile it to create a product build. This involves integrating various code modules and ensuring they work together as intended.
- Test The application or product undergoes rigorous testing to identify any bugs or issues. This includes unit, continuous integration, and end-to-end tests to ensure the product functions correctly.
- Release After successful testing, the product is prepared for release. This involves packaging the software and making it ready for deployment.
- Deploy: In this phase, the team deploys the product to the production environment. This could be a cloud server, a data center, or any other infrastructure setup that supports the application.
- Operate: Once deployed, the operations team manages the application in the live environment, ensuring its availability, performance, and security.
- Monitor Continuous monitoring is essential to tracking the product’s performance and health. Monitoring tools gather data on how the application functions and identify potential issues.
Let's break down the complete process:
As you can see, DevOps is a comprehensive approach encompassing planning, coding, building, testing, releasing, deploying, operating, and monitoring. This diffrent DevOps lifecycle stages allows companies to deliver high-quality products quickly and reliably, enhancing their ability to serve customers efficiently and compete in the market.
DevOps Automation
DevOps automation entails using tools, technologies, and processes to automate various stages of the software development lifecycle (SDLC) and the operations workflow. It’s the secret sauce that eliminates manual, repetitive tasks and supercharges efficiency at every level.
DevOps automation encompasses infrastructure provisioning, code compilation and testing, deployment, monitoring, and more. Organisations can achieve faster, more reliable software delivery through automation. According to the Global State of IT Automation 2024, 82% of respondents are looking forward to updating or expanding their IT automation tools.
Automation, in turn, helps them stay competitive and responsive to market demands. That’s not all. The hidden benefit is that DevOps automation allows to include more strategic work by freeing time. This way, one can focus on other things, such as enhancing features and improving user experience. That’s what sells, after all!
Continuous Feedback and Improvement:
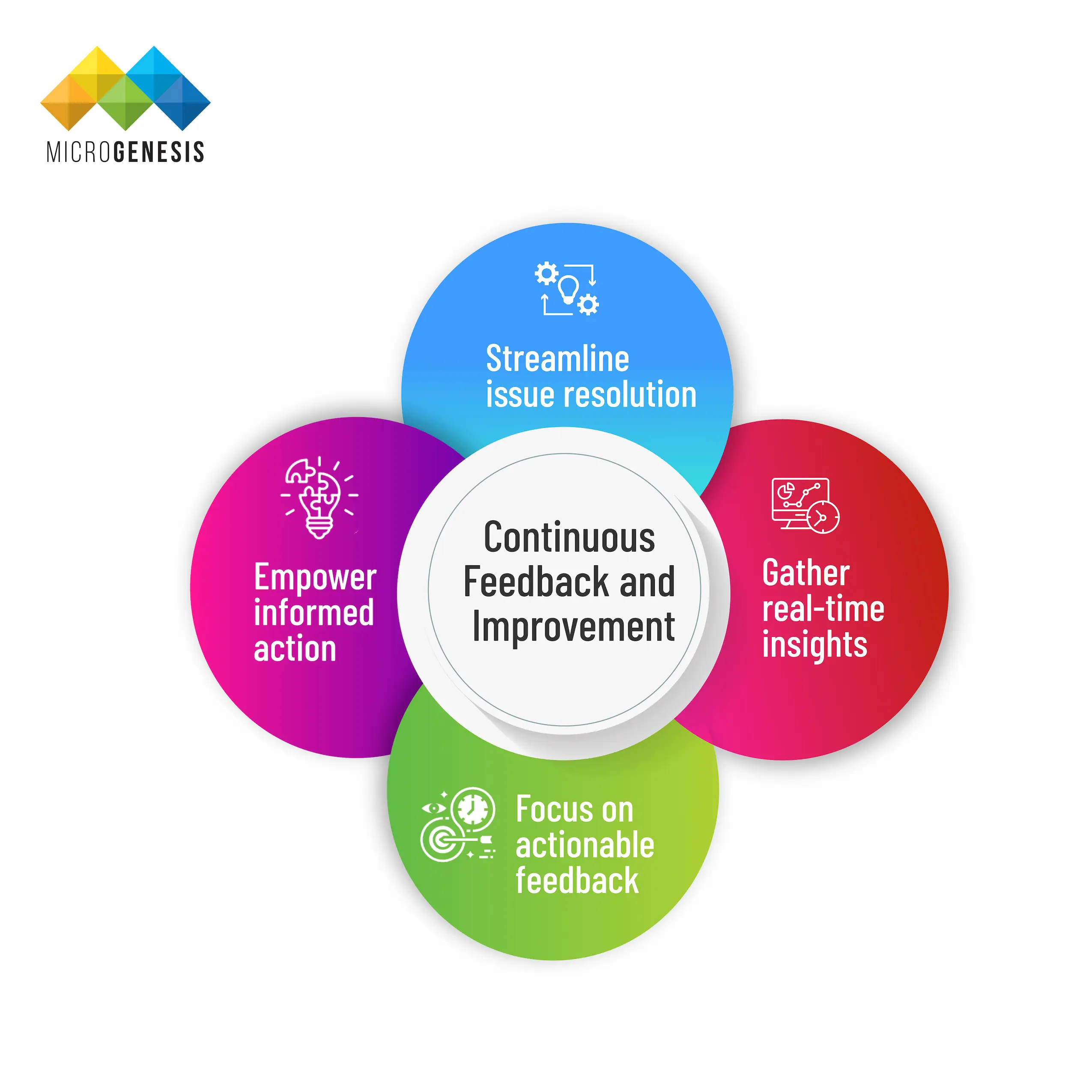
DevOps software development thrive on a culture of continuous learning and adaptation. This means constantly gathering feedback to refine processes, applications, and team member skills. This feedback loop allows teams to stay agile, respond quickly to evolving needs, and deliver software faster.
- Gather real-time insights: Continuously collect data on code changes as they progress through the pipeline.
- Empower informed action: Share this data with relevant teams to facilitate informed decision-making.
- Streamline issue resolution: Establish clear procedures for addressing problems and implementing ongoing improvements.
- Focus on actionable feedback: Analyze data to identify critical trends and reduce irrelevant information. Continuously measure success to track progress.
You can strengthen your DevOps feedback loop with these critical practices:
Continuous feedback is a DevOps superpower:
The approach that seeks feedback is applied across all DevOps principles and stages, from planning to monitoring. Feedback can come from various sources during continuous planning, such as post-deployment usage data, customer reviews, incomplete user stories, and user behaviour analysis. By incorporating this feedback, you can continuously refine your development process.
Measuring DevOps Success
Like any other software, several metrics can be regarded as the industry standard for evaluating the success of software delivery in an organisation. These can be your secret weapons to quickly spotting bottlenecks that may be slowing down your delivery process. Identifying errors in deployed code that cause failures also becomes much easier.
The insights provided by DevOps metrics are data-driven, which can help you improve continuously and deliver more value to your customers.
DORA, Google’s DevOps Research and Assessment team, has identified four key metrics, briefly discussed below, along with the other seven metrics, to help you measure your team’s performance improvement.
- Deployment Frequency: Have you ever wondered how often you deploy new features and fixes? The frequency of deployments, or deployment frequency, is among the defining metrics in DevOps. It helps understand how quickly an organisation can deliver the promised value to its customers. Here’s a breakdown of deployment frequency based on performance levels:
- Elite Teams: Achieve on-demand deployments, meaning their software is constantly in a releasable state and ideally deployed daily. This signifies a highly agile and low-risk development process.
- High-Performing Teams: Deploy frequently, potentially several times a week. Smaller deployments minimise risk and enable continuous delivery, allowing quicker feedback and iteration.
- Low-Performing Teams: Deploy infrequently, with significant releases happening over months. This approach can hinder velocity and significantly increase the impact of deployment failures.
The Benefits of Frequent Deployments:
- Reduced Risk: Smaller deployments help minimise the potential damage that bugs or errors can cause. In case of an issue, it becomes easier to identify and fix it within a smaller codebase.
- Faster Feedback: Frequent deployments allow quicker user feedback, enabling teams to iterate and improve features rapidly.
- Increased Agility: The ability to deploy frequently empowers teams to adapt to changing requirements and market demands more readily.
How to Increase Your Deployment Frequency:
- Shrink Deployment Size: Focus on releasing a single feature or change at a time rather than bundling multiple features into large deployments. This minimises the complexity and risk associated with each deployment.
- Automate Testing: Implement automated testing processes to ensure the quality and functionality of your code before each deployment. This streamlines the deployment process and frees up team resources.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Utilizing IaC tools to automate infrastructure provisioning and configuration ensures consistent environments and helps simplify the deployment process.
DevOps and Organizational Change
By now, you would have understood that DevOps is not limited to simple practices and tools for operations and development teams. It goes beyond that, enabling organisations to understand the importance of changing management to ensure a DevOps successful implementation.
Before getting into the best practices and examples of implementing organisational change management in DevOps, let us have a look at the benefits related to the same:
- Fewer crashes: By planning changes carefully, there’s less risk of something going wrong and causing downtime.
- Teamwork makes the dream work: Everyone involved (like the drivers and mechanics) is on the same page about what’s happening, so they can work together effectively.
- Following the rules: Change management helps ensure everything stays compliant and above board.
- Learning from experience: By tracking changes, the team can see what worked well and what didn’t, which helps them improve for next time.
- Adapting on the fly: When the race (or business needs) change, the pit crew (or DevOps team) can adjust their routine to keep up.
Here, we have discussed some best practices for implementing organisational change management in DevOps:
- Clear Communication: Just like the pit crew needs to know exactly what’s happening during a stop, the importance of strong communication between development and operations teams (think drivers and mechanics) cannot be overstated. Chat apps, video calls, and DevOps collaboration software can keep everyone informed.
- DevOps Mindset: As reiterated several times, DevOps is primarily about teamwork! A DevOps culture is rooted in DevOp collaboration, automation, and constantly learning from experiences. It means encouraging experimentation and innovation and being open to improvement.
- Executive Buy-in: The team owner (executives) must see the value of a good pit crew (DevOps). Build a strong business case demonstrating DevOps’s benefits, like faster deployments and fewer crashes. Keep them engaged and show them how DevOps helps the organisation win the race.
- Continuous Improvement: The best pit crews constantly refine their routine based on experience. In DevOps, this means having a culture of constant improvement. Review processes regularly, monitor performance, and gather feedback to identify areas for improvement. Embrace automation and data analysis to learn from mistakes and make adjustments based on what works and what doesn’t. This keeps your software running at peak performance.
Now let us understand it better with the help of some examples given below:
A, Speeding Up Pit Stops (CI/CD)
Imagine constantly improving your pit stop routine. Change management helps plan and automate these “mini-changes” to make them smoother and faster, getting the car (your.) back on track quicker.
Read more about the five best CI/CD tools for your team here.
B. Building with Blueprints (Infrastructure as Code)
Think of your car’s design. Change management ensures everyone follows the exact blueprint (code) when building or fixing parts of the vehicle (infrastructure). This reduces errors and keeps everything consistent.
C. Adapting on the Fly (Agile Development)
The race (business needs) can change. Change management helps your pit crew (team) adapt their routine quickly by working together in short bursts and incorporating feedback to keep the car (software) running smoothly.
D. Talking it Out (ChatOps)
Clear communication is critical during a pit stop. Change management encourages using chat tools to keep everyone informed and resolve issues faster, getting the car back in the race sooner.
E. Keeping an Eye on the Engine (Monitoring and Analytics)
Monitoring the car’s vitals (system performance) is important for the entire process. Change management helps establish clear guidelines for tracking these vitals and fixing any problems that arise quickly, keeping the car running smoothly.
Security in DevOps
As discussed previously, organisations often have separate departments for software development and IT operations. These teams working independently may create challenges when integrating new features or fixing bugs.
Enter DevOps as the bridge between the two. DevOps promotes collaboration between development and operations by opening up mandatory communication throughout the entire software development lifecycle (DevOps SLDC). Developers write code with the needs of IT operations in mind, ensuring features are robust and function smoothly and securely for the end users.
With DevOps, it is now possible to ensure that new features and bug fixes can be released more frequently in smaller increments. This continuous delivery approach, facilitated by DevSecOps minimises disruption to business operations. Additionally, security is a core consideration from the beginning, reducing the risk of vulnerabilities in the final product. In the face of growing threats from data breaches, more and more companies are seen adopting DevSecOps to achieve agile development techniques with improved security. According to DataBridge Market Research, the DevSecOps market is expected to reach $23.16 billion by 2029, translating to nearly 31.5% CAGR 2022-2029.
Overall, DevOps creates a more streamlined and efficient software development process. By working together, development and IT teams can deliver a faster, more reliable, and ultimately more secure software experience for everyone involved.
Learn more about DevSecOps here.
DevOps Collaboration and Communication
Sometimes, separate development and operations teams can lead to a communication gap. This "siloed" approach often leads to finger-pointing and delays when integrating new features or fixing bugs.
DevOps tackles this by breaking down these silos and promoting collaboration between development, operations, and other teams. Everyone works together from the start, focusing on the same goal: delivering a high-quality product on time and within budget.
Communication is vital in this collaborative environment. Traditionally, development and operations speak different "languages," making it difficult to discuss problems or needs. DevOps encourages open communication throughout the entire development process. This means developers consider operational needs when building features, ensuring a smooth and secure experience for end users.
There are several ways to promote communication and teamwork in DevOps:
- Cross-functional teams These teams combine developers, DevOps test, operations personnel, and others. Everyone contributes to a shared codebase, fostering better understanding and communication. Building custom DevOps in test automation frameworks creates a knowledge silo, hindering new team member onboarding and slowing down overall efficiency.
- Full-stack developers These developers can handle tasks beyond coding, like testing or database administration. This versatility improves communication within the team.
- Automatiom Automating tasks like security testing reduces the workload and allows for faster deployments. This frees up time for teams to collaborate on more complex issues.
The bottom line is that communication and collaboration are essential for success in today's fast-paced development environment. By breaking down silos and fostering teamwork, DevOps culture ensures a smoother, more efficient agile development DevOps process for everyone involved.
Scaling DevOps: Growing Your Practices
DevOps agile software development is fantastic for streamlining development and operations, but what happens when your organisation grows? Here’s how to effectively scale your DevOps practices, with a strong emphasis on fostering collaboration DevOps across all teams:
- Embrace Automation:
Repetition is the enemy of scaling. To avoid this, you must automate everything you can, from infrastructure provisioning to testing and deployment. This frees up your team to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Focus on Smaller Deployments:
Break down significant feature releases into smaller, more manageable chunks. This minimises risk and allows for faster feedback loops, ensuring a smoother delivery process.
- Invest in Monitoring and Analytics:
Implementing powerful monitoring tools to track performance metrics can be one way to identify potential bottlenecks. This allows you to address issues proactively and helps optimise your DevOps pipeline.
- Cultivating a Culture of Collaboration:
It is now a fact that DevOps thrives on teamwork. Encourage open communication between development, operations, and other teams.
You can use some tips for ensuring collaboration across departments:
- Shared Tools and Strategies:
- Cross-functional Collaboration:
- Creative Communication Channels: Think outside the box! Consider asynchronous communication methods, like podcasts or internal knowledge bases, to cater to globally distributed teams or those with different work styles.
The tools and strategies you use to communicate may vary based on where you sit in your company, but there are a few best practices that engineering teams use that can be applied to non-engineering teams. Consider pairing up on projects, even for non-coding tasks like design or marketing campaigns.
Explore tools like GitLab that can be used for collaborative project management across teams, even for non-technical users.
Ultimately, it is essential to remember that scaling DevOps is a journey, not a destination. By adopting these practices and continuously iterating, you can ensure your DevOps approach grows alongside your organisation, with collaboration DevOps at the core.
DevOps Leadership and Governance
Some organisations believe that DevOps is best used to speed up the process. While it is a powerful approach for streamlining software development (DevOps SLDC), speed shouldn’t come at the expense of control. The key to maximising your DevOps investment lies in understanding the importance of DevOps governance. This framework establishes responsible practices, ensuring your organisation gets the full benefits of a agile software development and DevOps process.
Here are some examples of the same:
- Promotes Risk Awareness: New initiatives always carry some risk. DevOps governance helps everyone involved understand potential problems and how to mitigate them. This fosters collaboration and ensures controls are seen as safeguards, not roadblocks.
- Improves Compliance: Every industry has regulations to follow. DevOps governance helps ensure your DevOps practices align with those regulations. This includes automating processes and change management to minimise compliance risks.
- Secures Development: Governance establishes precise access controls. Developers and testers can only access the necessary resources, reducing the risk of unauthorised changes or security breaches.
- Eases Code Management: Continuous delivery can lead to errors. DevOps governance promotes the “Cleanroom model,” which ensures proper tracking and monitoring of code changes. This prevents the introduction of bugs or security vulnerabilities.
Most organisations are realising the importance of DevOps and are incorporating it into their systems. But to truly succeed, organisations need to balance the benefits of speed with proper controls. DevOps governance is quintessential for maximising return on investment and ensuring your development process is secure and compliant.
Related posts
The Switch to Atlassian Jira
Difference Between Jira and GitHub
Jira and GitHub are two of the most popular tools in the software development world, each catering to different aspects of the development lifecycle. Jira is...
Trello vs. Jira: How to Choose and Integrate Them Effectively
Choosing between Trello and Jira can be challenging when searching for the ideal project management tool for your enterprise. Both tools have distinct...