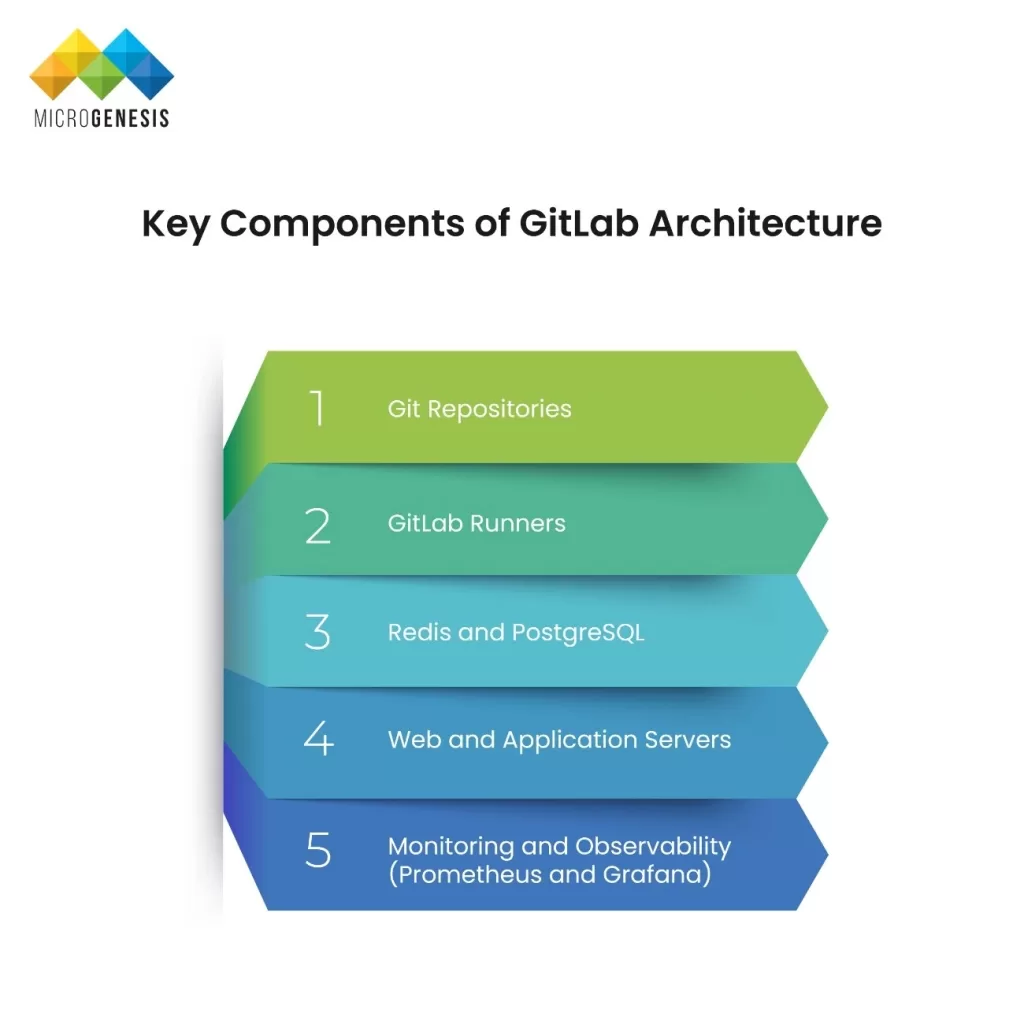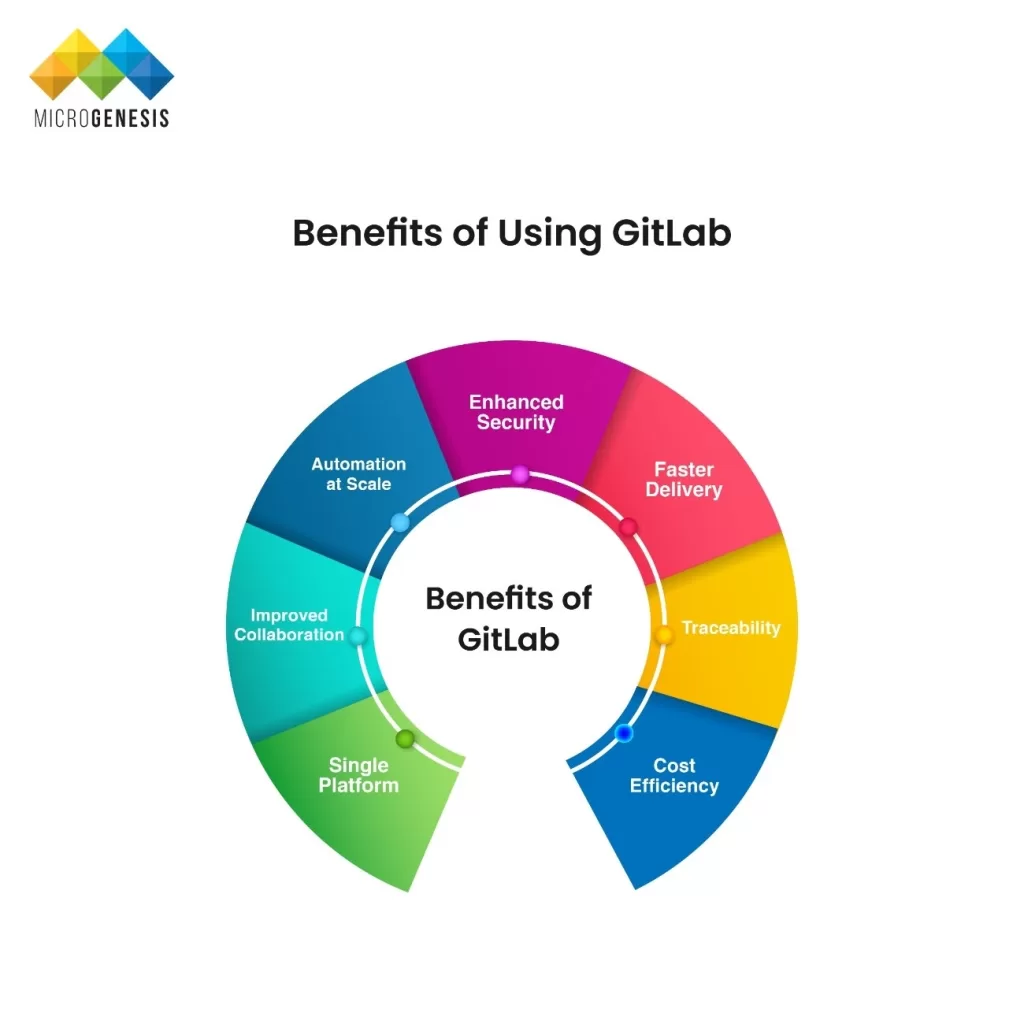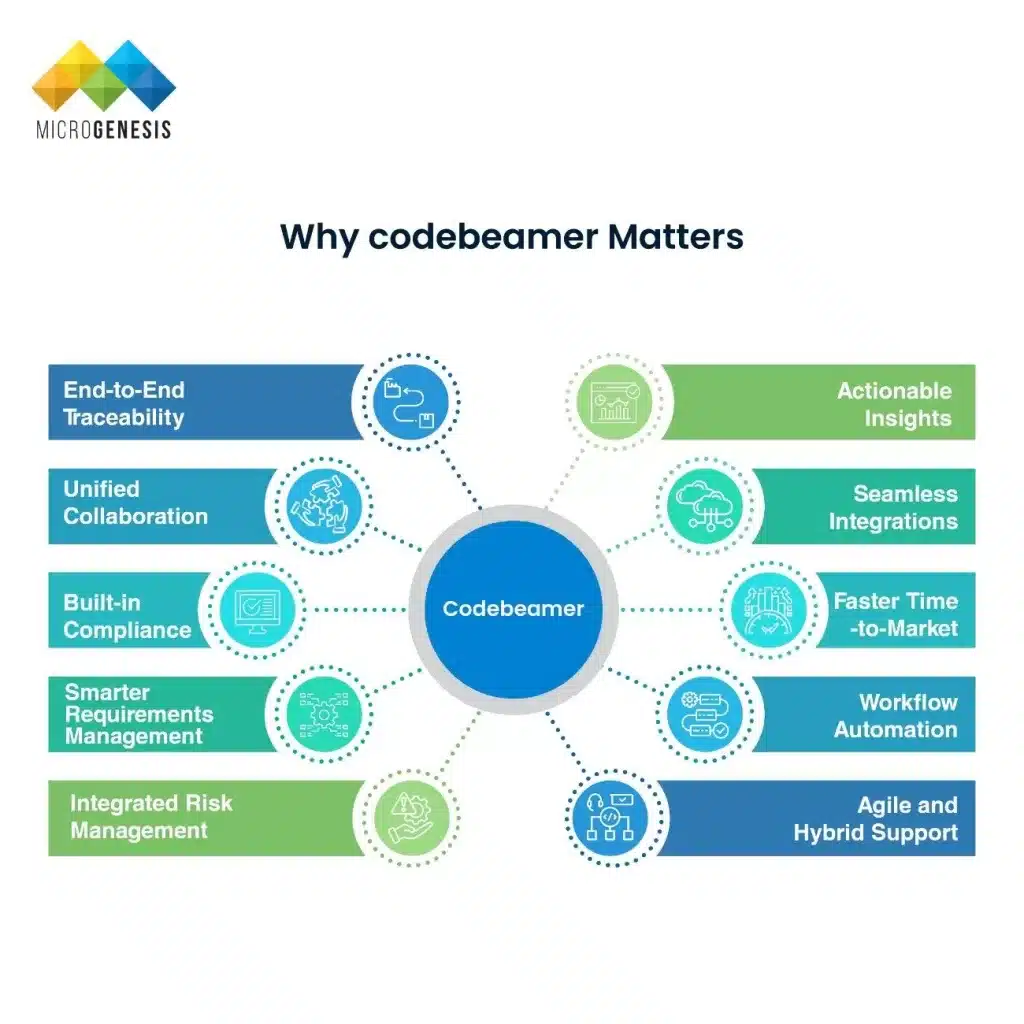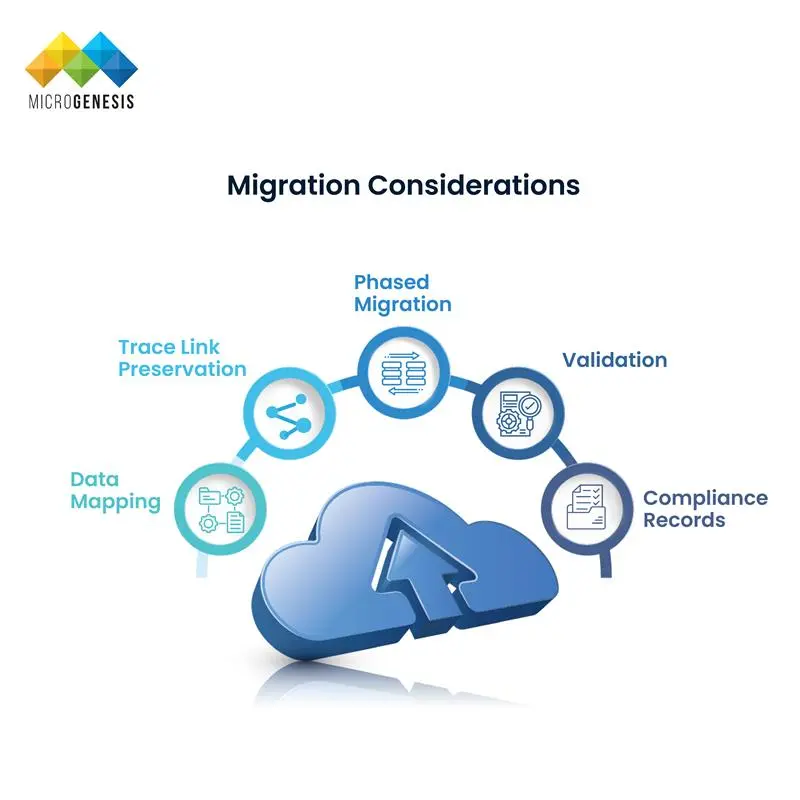
Optimizing IT Management for Modern Enterprises: Building Resilient, Scalable, and Secure Operations
by Chandra Sekaran | Nov 17, 2025 | Guides
Optimizing IT Management for Modern Enterprises: Building Resilient, Scalable, and Secure Operations
Home > Guides
Table of Contents
Introduction
In the modern enterprise, technology forms the foundation of nearly every business function — from customer engagement and analytics to logistics and compliance. As digital ecosystems expand, so too does the complexity of managing them.
Today’s IT leaders face a dual challenge: supporting business growth while maintaining seamless operations, security, and performance. Traditional models of reactive maintenance and isolated support teams no longer suffice. Instead, organizations are adopting integrated IT management frameworks — designed to deliver stability, efficiency, and agility in a rapidly evolving technological landscape.
This comprehensive guide explores how organizations can strengthen and modernize their IT management approach. It covers core components of IT operations, governance frameworks, strategic benefits, challenges, and future trends, providing a complete roadmap for building an intelligent, resilient IT environment.
Understanding IT Management in the Modern Enterprise
1.The Evolution of IT Operations
Over the past two decades, IT has transformed from a support function to a strategic enabler of innovation. The shift toward cloud computing, mobility, and automation has redefined IT management — emphasizing continuous optimization, user experience, and business alignment.
Modern IT management now involves:
- End-to-end monitoring of infrastructure, applications, and networks
- Cloud orchestration and resource governance
- Cybersecurity risk management
- Data lifecycle and compliance oversight
- Performance analytics and predictive insights
In essence, IT management is no longer about fixing problems — it’s about preventing them, optimizing continuously, and aligning technology outcomes with business goals.
2.The Business Value of Effective IT Management
Strong IT management contributes directly to organizational performance by:
- Ensuring business continuity through proactive monitoring and risk mitigation
- Enhancing employee productivity with reliable systems and collaboration tools
- Reducing operational costs via automation and intelligent resource allocation
- Supporting compliance and data integrity across increasingly complex digital ecosystems
- Enabling faster innovation cycles through streamlined infrastructure and DevOps practices
Effective IT management transforms technology from an operational necessity into a competitive differentiator.
Key Objectives of Modern IT Management

The goals of IT management have evolved from operational control to strategic orchestration. Modern IT functions pursue five interdependent objectives:
1.Operational Resilience
Enterprises rely on technology for every core process. IT management ensures resilience by integrating redundancy, monitoring, and disaster recovery into the fabric of operations.
A resilient IT environment can detect faults early, reroute workloads, and recover automatically — minimizing business disruption.
2.Security and Compliance
The surge in cyber threats and data protection regulations means IT governance must embed security into every process. Continuous vulnerability scanning, policy enforcement, and access controls form the foundation of digital trust.
3.Cost Optimization
Budgets are under constant scrutiny. IT management focuses on balancing performance and cost — leveraging cloud elasticity, virtualization, and automation to avoid overprovisioning and unnecessary spending.
4.Scalability
Scalable IT frameworks support business growth seamlessly. Whether onboarding 1,000 users or expanding into new regions, scalable infrastructure adapts without complex redesign.
5.Strategic Alignment
Technology must serve business outcomes — not operate in isolation. Modern IT management ensures strategic alignment through transparent governance, cross-functional collaboration, and continuous stakeholder communication.
Core Components of Effective IT Management

1.Infrastructure and Network Oversight
Infrastructure forms the backbone of IT operations — encompassing physical servers, virtual machines, cloud instances, and network hardware.
Effective management involves:
- Continuous monitoring: Real-time visibility into CPU, storage, and network utilization.
- Preventive maintenance: Automated patching and configuration management.
- Redundancy: Failover systems and clustering for high availability.
- Capacity planning: Data-driven forecasting for resource allocation.
An optimized infrastructure strategy supports faster processing, lower latency, and greater uptime — ensuring end-users remain productive and connected.
2.Cloud and Hybrid Environment Management
Cloud adoption has transformed how organizations deploy, scale, and secure their IT environments. However, hybrid ecosystems — combining on-premises systems with public and private clouds — add layers of complexity.
Key priorities include:
- Cost governance: Monitoring cloud spend and rightsizing instances.
- Security consistency: Extending encryption and IAM (Identity Access Management) across platforms.
- Automation: Leveraging Infrastructure as Code (IaC) to deploy environments rapidly and uniformly.
- Visibility: Unifying monitoring across multiple clouds using centralized dashboards.
Enterprises increasingly use multi-cloud orchestration platforms to harmonize workloads and reduce vendor lock-in.
3.Cybersecurity and Risk Governance
Cybersecurity is at the center of modern IT management. Beyond protecting systems, security must be measurable, auditable, and continuous.
Core elements include:
- Endpoint protection: Safeguarding devices from malware and phishing.
- Threat detection: Using SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) tools for real-time alerts.
- Incident response: Defined workflows for rapid containment and recovery.
- Compliance auditing: Ongoing monitoring for GDPR, HIPAA, or ISO 27001 alignment.
A unified risk governance framework integrates these controls, ensuring security policies evolve as threats do.
4.Data Management and Continuity
Data is the lifeblood of business operations. Managing its availability, accuracy, and recovery is essential.
Strong data governance includes:
- Backup automation: Scheduled, encrypted backups stored across regions.
- Disaster recovery planning: Regular failover testing and documented recovery objectives (RPO/RTO).
- Data lifecycle control: Defining retention, archiving, and disposal policies.
- Replication and redundancy: Ensuring critical data remains accessible during outages.
Organizations that invest in reliable backup and recovery systems reduce downtime from days to minutes — safeguarding both reputation and revenue.
5.Application and Performance Optimization
Modern applications are distributed, containerized, and continuously updated. Managing their performance requires both technical precision and automation.
Best practices include:
- Load testing: Assess scalability under peak conditions.
- Monitoring APM metrics: Latency, transaction times, and error rates.
- Version control and patching: Ensuring all components remain secure and current.
- Microservices management: Orchestrating APIs and dependencies across environments.
Consistent application performance directly impacts user experience and business outcomes — making this a core IT management priority.
Advantages of a Proactive IT Management Framework

1.Reliability and Uptime
Proactive monitoring minimizes disruptions by detecting anomalies before they escalate. Real-time alerts, predictive analytics, and automated responses contribute to continuous availability.
2.Cost Efficiency
Automation, virtualization, and cloud resource governance eliminate redundant expenses and optimize infrastructure utilization.
Predictable operational costs replace capital-heavy investments in hardware and maintenance.
3.Enhanced Security Posture
Integrated security frameworks safeguard networks, applications, and endpoints through centralized visibility and policy enforcement.
Continuous monitoring helps organizations adapt quickly to evolving threats.
4.Scalability and Agility
A well-structured IT environment can expand resources dynamically — supporting business growth without re-architecting entire systems.
5.Strategic Insight
Centralized data and reporting provide IT leaders with real-time visibility into performance metrics, user behavior, and financial impact — supporting data-driven decision-making.
Building an Effective IT Management Model
1.Governance Framework
A clear governance structure defines ownership, accountability, and escalation paths.
Governance should include:
- Defined performance metrics and KPIs
- Documented policies for change and configuration management
- Regular compliance and risk reviews
This ensures transparency, accountability, and alignment with organizational objectives.
2.Technology Integration
Integrating tools across IT operations enables cohesive management. Key integrations include:
- Monitoring and observability platforms
- IT service management (ITSM) systems
- Security information and event management (SIEM) tools
- Automation and orchestration engines
Unified visibility across these systems eliminates silos and supports end-to-end control.
3. Automation and Artificial Intelligence
Automation is the cornerstone of modern IT management. Tasks such as patching, alerting, and backup can be automated to reduce manual effort and human error.
AI-driven analytics further enhance this model by predicting failures, optimizing workloads, and automating incident response — a concept known as AIOps (Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations).
4.Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing
Cross-functional collaboration is critical to maintaining efficiency. Documentation, wikis, and integrated communication tools ensure institutional knowledge is shared across teams — reducing duplication and response times.
Measuring IT Management Performance
Continuous improvement in IT management relies on accurate and consistent performance measurement. Tracking the right metrics helps organizations evaluate how efficiently their systems operate, how quickly issues are resolved, and how effectively technology supports business goals.
Below are key performance indicators (KPIs) that provide valuable insight into IT operations and service quality:
- System Uptime (%): Reflects the reliability and availability of critical systems. High uptime ensures smooth business operations and user productivity. Many organizations target 99.9% or higher for mission-critical applications.
- Mean Time to Detect (MTTD): Measures how quickly issues are identified once they occur. A lower MTTD indicates effective monitoring and alerting systems capable of spotting problems before they escalate.
- Mean Time to Resolve (MTTR): Tracks the average time taken to restore normal operations after an incident. Reducing MTTR requires strong coordination, automated workflows, and clear escalation processes.
- Security Incident Rate: Represents the frequency and severity of detected threats or vulnerabilities. Regularly analyzing this rate helps assess the effectiveness of security measures and identify areas needing stronger protection.
- Cost per User or Device: Evaluates the efficiency of resource utilization by comparing operational costs to the number of supported users or endpoints. This metric helps optimize budgets and identify opportunities for automation or consolidation.
- User Satisfaction (CSAT/NPS): Gauges how end-users perceive IT responsiveness, reliability, and overall experience. Higher satisfaction levels often indicate smoother processes, faster support, and better communication.
Regular performance reviews and analytics-driven reporting ensure that IT teams remain aligned with business priorities. By continuously analyzing trends and adjusting strategies, organizations can improve operational reliability, reduce costs, and enhance the user experience — turning IT performance into a measurable driver of business success.
Common Challenges in IT Management

Despite advancements in technology and process automation, many organizations still face obstacles in managing their IT environments efficiently. These challenges often arise from the growing complexity of digital ecosystems, evolving security risks, and organizational limitations. Understanding these challenges — and proactively addressing them — is essential for maintaining resilience and operational stability.
1.Complexity of Multi-Platform Environments
As organizations adopt hybrid and multi-cloud infrastructures, IT environments now span data centers, public clouds, SaaS platforms, and edge devices. Managing this diversity can be challenging — different tools, configurations, and standards often lead to fragmented visibility and inconsistent performance.
Solution:
Implement centralized dashboards and unified monitoring tools that provide real-time visibility across platforms. Establish standardized policies, naming conventions, and configuration baselines to maintain uniformity and reduce integration errors.
2.Evolving Cyber Threats
Cybersecurity remains a top concern as threats evolve in scale and sophistication. Ransomware, phishing, insider threats, and zero-day vulnerabilities continue to test organizational defenses. The shift toward remote work and IoT devices has further expanded the attack surface.
Solution:
Adopt zero-trust architecture, enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA), and integrate continuous threat monitoring. Conduct regular penetration tests and security audits to identify vulnerabilities before attackers do. Embedding security into every IT process ensures stronger, more adaptive protection.
3.Resource and Skill Constraints
The rapid pace of technological change has created a persistent skills gap in areas such as cloud engineering, cybersecurity, and AI-driven operations. Limited staffing and expertise can slow innovation and increase operational risk.
Solution:
Invest in continuous learning programs and professional certifications to upskill internal teams. Encourage knowledge-sharing across departments and leverage partnerships with external specialists or managed providers for advanced capabilities when needed.
4.Resource and Skill Constraints
Introducing new tools, automation frameworks, or management processes often faces internal resistance. Employees may fear job displacement, or leadership may be reluctant to overhaul established workflows. Such resistance can delay modernization efforts and limit adoption.
Solution:
Implement a structured change management strategy that emphasizes transparency, communication, and leadership involvement. Demonstrate the value of change through pilot programs, early wins, and success stories that encourage wider acceptance.
5. Regulatory Complexity
Organizations operating across multiple regions must navigate complex and evolving compliance requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, ISO 27001, and SOC 2. Managing data privacy, retention policies, and audit readiness can be time-consuming and error-prone without the right systems in place.
Solution:
Integrate compliance automation into IT workflows to continuously track policy adherence. Use audit-ready reporting tools to simplify documentation and maintain real-time visibility into compliance status. This approach minimizes regulatory risk while reducing manual effort.
Emerging Trends in IT Management

The landscape of IT management continues to evolve as new technologies, business models, and regulatory pressures reshape how organizations approach infrastructure, security, and innovation. Modern IT leaders are shifting from reactive, siloed operations to integrated, data-driven ecosystems that emphasize intelligence, automation, and sustainability.
The following trends are shaping the future of IT management across industries:
1.AI-Driven Operations
Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations (AIOps) is revolutionizing how organizations manage complex digital ecosystems. By leveraging machine learning and big data analytics, AIOps platforms automatically detect anomalies, forecast outages, and trigger self-healing actions without human intervention.
This shift transforms IT management from a reactive approach to predictive and autonomous operations. For example, AI can identify early signs of performance degradation in servers or networks and initiate corrective measures before users are affected.
As organizations adopt more hybrid and cloud-based systems, AIOps will become essential for maintaining visibility, reducing mean time to resolution (MTTR), and improving overall efficiency.
2.Cloud-Native and Edge Computing
IT management is no longer confined to centralized data centers. The rise of cloud-native architectures and edge computing has extended management responsibilities to distributed systems located closer to end-users and data sources.
Cloud-native technologies, including containers and microservices, allow applications to scale dynamically and run efficiently across multiple environments. Meanwhile, edge computing enables data processing to occur near the source — minimizing latency and improving real-time responsiveness for IoT and industrial systems.
These developments demand decentralized yet coordinated management, where IT teams can maintain consistency, performance, and security across a geographically dispersed infrastructure.
3.Zero-Trust Architectures
As cyber threats grow more sophisticated, organizations are abandoning traditional perimeter-based security models in favor of Zero-Trust Architecture (ZTA).
The principle of “never trust, always verify” ensures that every user, device, and connection — internal or external — is continuously authenticated and authorized before accessing resources. This minimizes the risk of insider threats, credential theft, and lateral movement of attacks within networks.
Zero-trust adoption requires integration between identity management, endpoint security, and network monitoring, supported by automation to enforce policies in real time. In the future, ZTA will be a foundational requirement for secure digital transformation.
4.Sustainable IT Practices
Sustainability has become a key pillar of corporate strategy, and IT operations play a major role in achieving it. Green IT practices focus on reducing environmental impact through energy-efficient infrastructure, optimized resource usage, and responsible hardware lifecycle management.
Organizations are adopting cloud services powered by renewable energy, extending hardware lifespans through predictive maintenance, and implementing virtualization to reduce data center footprints.
Beyond environmental benefits, sustainable IT also delivers economic efficiency — lowering energy costs and aligning technology investments with long-term ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals.
5.Integration of Security and IT Operations (SecOps)
Traditionally, IT operations and cybersecurity teams worked independently, leading to communication gaps and delayed incident responses. The emergence of SecOps — the integration of security and operations — bridges this divide.
By combining real-time monitoring, automation, and cross-team collaboration, SecOps enables faster detection, analysis, and remediation of threats. It also enhances operational visibility, ensuring that every security event is addressed within the broader context of system performance and availability.
This unified model strengthens overall resilience, helping organizations maintain compliance and mitigate risks more effectively in an increasingly interconnected IT environment.
The Future of IT Management
The next generation of IT management will be autonomous, intelligent, and adaptive.
Technologies like AIOps, quantum computing, and hyper-automation will redefine how infrastructure and applications are monitored and maintained.
Organizations will increasingly adopt self-healing systems, where issues are identified and resolved automatically. Compliance will become continuous, with built-in governance embedded into workflows.
Ultimately, IT management will move beyond operational stability to become a strategic ecosystem — one that anticipates business needs, reduces risks, and accelerates innovation.
Conclusion
Effective IT management is no longer about keeping systems running — it’s about empowering business growth through stability, intelligence, and adaptability.
By integrating governance, automation, and analytics, organizations can achieve continuous visibility, optimize costs, and enhance resilience.
Whether managing on-premises infrastructure, cloud workloads, or distributed edge networks, a proactive approach to IT management ensures that technology remains a source of strength, not complexity.
The future belongs to enterprises that treat IT not as a background function, but as a strategic, data-driven foundation for innovation and long-term success.
Our Blogs